|
Following is the full text of the Report on the Implementation of the 2005 Plan for National Economic and Social Development and on the 2006 Draft Plan for National Economic and Social Development, delivered at the Fourth Session of the 10th National People's Congress on March 5, 2006:
Report on the Implementation of the 2005 Plan for National Economic and Social Development
And on the 2006 Draft Plan for National Economic and Social Development
National Development and Reform Commission
I. Implementation of the 2005 Plan for National Economic and Social Development
II. Overall Requirements and Main Targets for Economic and Social Development in 2006
III. Principal Tasks and Measures for Economic and Social Development in 2006
Fellow Deputies,
The National Development and Reform Commission has been entrusted by the State Council to submit this report to the Fourth Session of the Tenth National People's Congress (NPC) on the implementation of the 2005 plan for national economic and social development and on the 2006 draft plan for national economic and social development for your deliberation and approval and also for comments and suggestions from members of the National Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference.
I. Implementation of the 2005 Plan for National Economic and Social Development
Under the leadership of the Communist Party of China (CPC), the people of all our ethnic groups adopted and implemented a scientific outlook on development, improved macroeconomic regulation, worked hard together and forged ahead resolutely in 2005. The national economy did well, exhibiting fairly rapid growth and good performance with stable prices. The Plan for National Economic and Social Development adopted at the Third Session of the Tenth NPC was fully implemented.
1. The economy maintained steady and rapid growth. Economic activity became more stable. The GDP for the whole year amounted to 18.2321 trillion yuan, up 9.9%, and grew at a rate of 9.9% the first quarter, 10.1% the second, 9.8% the third and 9.9% the fourth. The added value created by large industrial enterprises increased 16.4% during the year, growing at a rate of 16.2% the first quarter, 16.5% the second, 16.2% the third and 16.4% the fourth.
Figure 1.
GDP During the Tenth Five-Year Plan Period
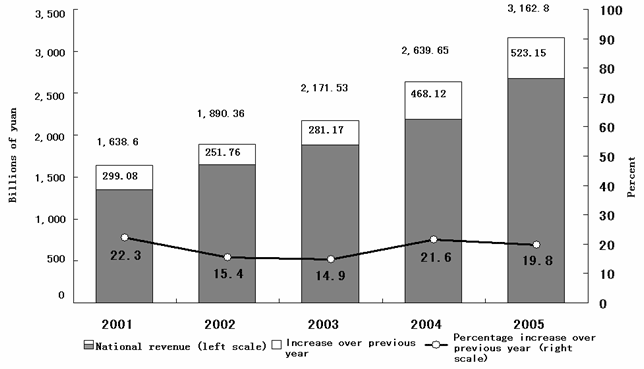
Economic development was more balanced. The growth rate was fairly high and prices were stable, with the consumer price index rising 1.8% for the whole year. Economic performance improved in step with economic growth. National revenue increased by 523.15 billion yuan or 19.8% for the year, and profits of large industrial enterprises rose by 22.6%. Shortages hampering economic growth were eased. Coal output reached 2.19 billion tons, up 9.9%; electricity generated reached 2.47 trillion kilowatt-hours, up 12.3%; the total of the number of power lines affected by power outages and the number of outages occurring during summer peak hours was 61% less than the previous year and the amount of power loss caused by outages was down by 66%; and transport of key materials was better ensured.
Figure 2.
National Revenue During the Tenth Five-Year Plan Period
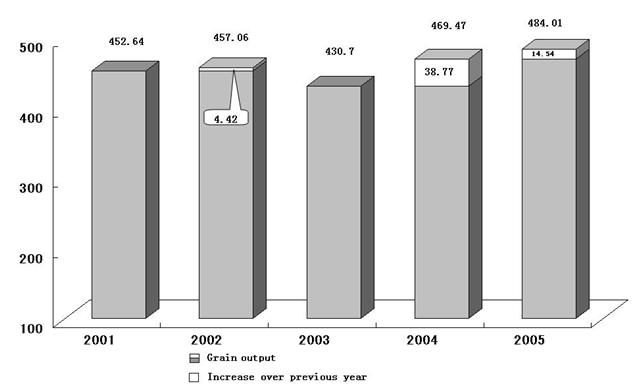
2. Further progress was made in industrial restructuring. Agriculture was strengthened. Last year, 297.5 billion yuan from the central government budget was spent on agriculture, rural areas and farmers, a year-on-year increase of 34.9 billion yuan. The acreage sown to grain rose by 2.67 million hectares over the previous year, and grain output totaled 484 billion kilograms, 14.54 billion kilograms more than the previous year. We continued to improve the quality of agricultural products, industrialize agricultural production, standardize agricultural operations, and concentrate the production of superior agricultural products in the most suitable areas. The acreage sown to high-quality special wheat accounted for 48% of China's total wheat acreage, up 4 percentage points year-on-year. Similarly, acreage of high-quality rice accounted for 64%, up 3 percentage points. The animal husbandry and aquaculture industries continued to grow.
Figure 3.
Grain Output During the Tenth Five-Year Plan Period
(Billions of kilograms)
Industrial restructuring was accelerated. Hi-tech industries developed rapidly, and the added value created by large hi-tech enterprises rose by 19.8%. A number of major projects for science and technology development and for industrial application of advances in science and technology were successfully implemented. Further progress was made in developing key technologies and increasing domestic manufacture of key equipment. The work of importing and assimilating large gas turbines, urban rail transit facilities, large hydroelectric generating units and pumped storage power generating units proceeded smoothly. Projects were launched to build million-ton ethylene plants domestically, and the demonstration project for a 750-kilovolt AC transmission line and transformer facility was completed. Corporate merger and reorganization was sped up; a number of outmoded production facilities that waste energy, create serious pollution or do not have conditions to ensure safe production were closed down; and the growth of investment in some overheated industries continued to decline.
Figure 4.
Added Value Created by Large Hi-tech Enterprises During the Tenth Five-Year Plan Period
(Billions of yuan)
Infrastructure development was intensified. Construction on the West-to-East Electricity Transmission Project, the South-to-North Water Diversion Project and other key projects progressed smoothly. The Qinghai-Tibet Railway was completed one year ahead of schedule. The projects to upgrade highways connecting county seats were basically completed. An additional 130,000 kilometers of highways, including 6,457 kilometers of expressways, were built. Newly built railways opened to traffic in 2005 totaled 1,203 kilometers, electrified railways 863 kilometers, and double-track railways 486 kilometers.
The service sector continued to develop steadily. IT application continued to expand in the government and in business. Development of emerging services such as telecommunications, modern logistics, community services, tourism, and conference and exhibition services was accelerated, and traditional service industries including commerce and trade, and food and beverage services enjoyed good growth.
3. The overall strategy for regional development was carried forward. The development of the western region proceeded smoothly, and ten key projects were launched there with total investment of 136 billion yuan. The Suining-Chongqing-Huaihua Railway was opened to traffic; construction on the western sections of the five vertical and seven horizontal national trunk highways began; the projects to build, renovate or expand ten airports in the western region, including those in Chongqing, Xining and Manzhouli, were completed; and construction of the Baise and Zipingpu dams was completed and water storage in their reservoirs was begun. Implementation of the strategy for revitalizing Northeast China and other old industrial bases made steady progress. We supported the expansion of competitive industries, such as the petrochemical, steel, major equipment, shipbuilding, automobile and auto parts industries, focusing on increasing domestic manufacture of major equipment and enhancing enterprises' capacity for independent innovation. Initial progress was made in the trial transformation of the economies of cities reliant on natural resources, and the work of renovating shantytowns was started. We worked out and implemented policy measures to energize the central region, resulting in further strengthening of the position of agriculture as the foundation of the economy, expansion of competitive industries, and strengthening of the role of large groups of cities in driving the development of surrounding areas. The eastern region continued to lead in the country's development, and its economic restructuring and the transformation of its pattern of economic growth had good results.
4. Further breakthroughs were made in economic restructuring. Trials of overall rural reform were carried out, the livestock tax was rescinded, and exemption of the agriculture tax was extended to 28 province-level localities. Reform of state-owned enterprises was deepened, and oversight of state assets was tightened. Further advances were made in reforming the management systems of the railway, civil aviation and tobacco industries, and reform of the postal service system was initiated. Policy measures were formulated and instituted to encourage, support and guide the development of the non-public sector of the economy. Reform of the mechanism for setting the RMB exchange rate was successfully implemented. Steady progress was made in reforming the shareholder structure of listed companies. Great strides were made in introducing the shareholding system in state-owned commercial banks. Comprehensive trials to deepen the reform of rural credit cooperatives were launched. The export rebate mechanism was improved. Trial VAT reform in the old industrial base of Northeast China proceeded smoothly. Reform of the investment system continued, and the system for approving and recording projects funded by enterprises were instituted nationwide. The plan for reforming the producer price of natural gas was put in place, a mechanism was established for coupling the price of coal to those of electricity and heating, and the water price reform continued steadily.
5. China opened further to the outside world. Import and export volume reached US$ 1.4221 trillion in 2005, a year-on-year increase of 23.2%. Exports accounted for US$762 billion, up 28.4%, and imports amounted to US$660.1 billion, up 17.6%. Export volume of electromechanical products rose 32% and new and high technology products by 31.8%. The service sector was opened further to foreign competition. Progress was made in discouraging the export of highly polluting products, resource products and products that consume excessive quantities of energy. We continued to make more and better use of foreign capital, with the amount of foreign direct investment actually used over the year totaling US$60.3 billion. The country's year-end foreign exchange reserves reached US$818.9 billion. Progress was made in encouraging enterprises to go global, and total overseas direct investment of Chinese enterprises (non-financial portion) over the year reached US$6.9 billion.
Figure 5.
The Import and Export Volume During the Tenth Five-Year Plan Period

6. Achievements were made in resource conservation and environmental protection. More efforts were made to save energy, water, materials and land, to comprehensively utilize resources, and to develop a circular economy. The first group of pilot projects for a circular economy was launched in key industries and sectors, industrial zones, and some areas. A policy of charging differential prices was adopted in some high power-consuming industries, state standards for water quotas were set for some high water-consuming industries, and energy efficiency standards were required for some products. Water consumption per 10,000 yuan of GDP dropped by 8.7%. Progress was made in extensively applying energy-efficient techniques in construction, producing new wall materials, saving lumber and using wood substitutes. People throughout the country became more aware of the depletion of natural resources and the need to conserve them.
We sped up work to prevent and control pollution in such key areas as the watersheds of the Huai, Hai and Liao rivers and Tai, Chao and Dianchi lakes, the Three Gorges Reservoir area, and along the routes of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Control of pollution caused by urban sewage, industrial wastewater, hazardous wastes, and sulfur dioxide emissions from thermal power plants was strengthened. A greater proportion of urban sewage was treated, and more industrial solid waste was comprehensively utilized. Air quality improved in some cities where the air had been seriously polluted. We returned 1.111 million hectares of cultivated land to forests, afforested 2.667 million hectares of barren or closed-off hills and uncultivated land, and returned 6.667 million hectares of grazing land to grassland. Progress was made in major ecological conservation projects, such as those to protect natural forest resources and bring the sources of dust storms affecting Beijing and Tianjin under control. We improved 8.38 million hectares of grassland affected by desertification, degeneration or alkalization, brought soil erosion under control in 4.2 million hectares of land, and restored the ecology in 72,000 hectares of mining areas. Protection of wildlife species and habitats was strengthened.
Figure 6.
Areas of Cultivated Land Returned to Forests, Barren Hills and Uncultivated Land Afforested, and Grazing Land Returned to Grassland During the Tenth Five-Year Plan Period
(Tens of thousands of hectares)
7. Science and technology, education, culture, health and other social programs developed in an all-round way. The Outline of the National Long- and Medium-Term Program for Scientific and Technological Development (2006-2020) was promulgated and implemented. The national innovation system, basic research, and the science and technology infrastructure were further improved. We successfully launched the Shenzhou VI manned spacecraft. Development of the Goodson-2 general purpose high-performance microprocessor chip and the genetically engineered inactivated AI vaccine for poultry was completed. Pest-resistant cotton was grown on 3 million hectares of land. We signed 265,000 technology-related contracts worth 151 billion yuan during the year, up by 13.2% over the previous year.
Compulsory education is now available in 95% of the country's populated areas. Progress was made in the program to make nine-year compulsory education basically universal and to basically eliminate illiteracy among young and middle-aged adults in the western region. We built, renovated or expanded over 2,400 boarding schools in rural areas and provided distance learning equipment for 160,000 rural primary and secondary schools and teaching centers. With funds of over 7 billion yuan from both central and local governments, 17 million poor students were given free textbooks and exempted from tuition and miscellaneous fees, and students living on campus were granted living allowances in 592 key counties designated for poverty-alleviation work, and more than 17 million poor students were provided free textbooks in the central and western regions. The construction of school buildings and practice laboratories for secondary vocational schools and county-level vocational education centers was accelerated. Steady progress was made in the 211 Project and the May 1998 Program for higher education.
Figure 7.
Proportion of the Areas Where Compulsory Education Was Available During the Tenth Five-Year Plan Period (%)
The system of public culture-related services was improved. Efforts to develop major cultural projects and to protect natural and cultural heritage sites were intensified. Almost every county has a cultural center and library. Progress was made in the project to extend radio and TV coverage to all rural villages, which now reaches 27 million more people. The Outline of the National Program to Develop Red Tourism was initiated. Extensive fitness programs were launched for the general public and smooth progress was made in building Olympic venues.
Establishment of the disease prevention and control system was basically completed. Development of the medical treatment system proceeded smoothly. We continued to build the rural health service system and improved the rural health infrastructure, centering on health clinics in towns and townships in the central and western regions. Trials of a new type of rural cooperative medical care system were extended to 671 counties with a total of 177 million rural residents. Development of urban community health services was accelerated. Preliminary achievements were made in preventing and controlling the spread of highly pathogenic avian influenza. We began work on a service system for rural family planning. The natural population growth rate was 5.89‰.
8. People's lives continued to improve. Urban per capita disposable income rose by 9.6% and rural per capita net income by 6.2% in real terms. Retail sales of consumer goods rose by 12.9%. Urban employment increased by 9.7 million, and the registered urban unemployment rate was 4.2%. The coverage of the social security system continued to expand, efforts were intensified to provide the "two guarantees" [guarantee of basic living allowances for workers laid off from state-owned enterprises and guarantee that retirees' pensions are paid on time and in full, tr.], and the basic livelihood of poor people in urban and rural areas was ensured. The work of incorporating basic living allowances for workers laid off from state-owned enterprises into the unemployment insurance system has been basically completed in nearly all parts of the country. Trials for improving the urban social security system in the northeast progressed smoothly.
Urban and Rural Incomes and the Engel Coefficient During the Tenth Five-Year Plan Period
|
Year |
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
2004 |
2005 |
|
Urban per capita disposable income (yuan) |
6,859.6 |
7,702.8 |
8,472.2 |
9,421.6 |
10,493 |
|
Real growth (%) |
8.5 |
13.4 |
9.0 |
7.7 |
9.6 |
|
Rural per capita net income (yuan) |
2,366.4 |
2,475.6 |
2,622.2 |
2,936.4 |
3,255 |
|
Real growth (%) |
4.2 |
4.8 |
4.3 |
6.8 |
6.2 |
|
Engel coefficient |
Urban families (%) |
38.2 |
37.7 |
37.1 |
37.7 |
36.7 |
|
Rural families (%) |
47.7 |
46.2 |
45.6 |
47.2 |
45.5 |
Figure 8.
Basic Old-age Insurance Coverage During the Tenth Five-Year Plan Period
Though progress was made in economic and social development, we still face many difficulties and challenges. Some longstanding and deep-seated problems are hindering sound development of the economy, such as limited capacity for independent innovation, imbalanced economic structure, extensive pattern of economic growth, increasing restraints imposed by resources and the environment, notable disparity between urban and rural economies, imbalanced economic and social development, systems and mechanisms that need further improvement, and an inadequate legal system. The current serious problems are as follows.
1) It has become very difficult to increase grain production and rural incomes. Resolving the problem of weak agricultural infrastructure requires fundamental changes, and there is little land available for increasing grain production by expanding acreage. Overall agricultural income remains low, there is considerable downward pressure on grain prices, increases in energy and raw material prices have raised the costs of agricultural production, and there are numerous factors preventing rural migrant workers in cities from earning more money.
2) Investment in fixed assets continued to rise too fast. Total fixed asset investment nationwide in 2005 increased by 25.7%, slower than the previous year, but still very fast. There are too many fixed asset investment projects under construction, and too many new ones are being started. Investment in some industries is expanding too fast, the pattern of distribution of investment among different industries is irrational, and there is pressure for overheated investment to rebound.
3) Adverse effects of surplus production capacity in some industries have begun to emerge. Prices for the products of these industries dropped and inventories grew, corporate profits shrank and losses mounted, and potential financial risk has increased.
4) Many problems vital to the immediate interests of the people have not yet been properly solved. Pressure on employment and reemployment has increased, the social security system needs to be improved, the income gap among some members of society is expanding, and little progress has been made in dealing with problems such as arbitrary educational charges, inadequate medical facilities and excessively high medical costs. People still complain bitterly about certain problems related to environmental protection, enterprise restructuring, land expropriation, housing demolition and resident relocation, and displacement of people to build reservoirs. Preventing and controlling the spread of highly pathogenic avian influenza and other major animal and plant epidemics continues to be an arduous task.
5) The production safety situation remains grim. Major coalmine and traffic accidents occur frequently, causing serious loss to people's lives and property. We must pay close attention to the above-mentioned problems, take vigorous measures and work conscientiously to solve them.
II. Overall Requirements and Main Targets for Economic and Social Development in 2006
The year 2006 is the first year for implementing the Eleventh Five-Year Development Guidelines and a year that represents a new historic point of departure for China. Success in all aspects of our work for this year is crucial for consolidating and continuing rapid yet steady economic development and smoothly implementing the Eleventh Five-Year Development Guidelines. To ensure economic and social development this year and get the Eleventh Five-Year Development Guidelines off to a good start, we must take Deng Xiaoping Theory and the important thought of Three Represents as our guide; follow the guiding principles set out at the Sixteenth National Congress of the CPC and the Fifth Plenary Session of the Sixteenth Party Central Committee; continue to take a scientific outlook to guide overall economic and social development; maintain the continuity and stability of our macroeconomic policies; work hard to accelerate reform and opening up; improve our capacity for independent innovation; promote economic restructuring and transformation of the pattern of growth; improve the quality and benefits of economic growth; continue to put problems affecting the vital interests of the people high on our agenda; properly balance reform, development and stability; and promote all aspects of socialist economic, political and cultural development and efforts to create a harmonious society.
On the basis of these requirements, we must follow the principles of maintaining stability in government policy with fine-tuning as needed, always keeping the big picture in mind while paying close attention to key areas, taking all factors into consideration in making overall plans, paying close attention to the well-being of the people, and staying firmly rooted in the present while looking ahead to the future in order to ensure successful economic and social development this year. Taking into consideration the necessity and feasibility of economic and social development, last year's actual performance, and the requirements of the Eleventh Five-Year Development Guidelines (draft), we have set the main targets for economic and social development in 2006 as follows.
- GDP growth around 8%. There are several major factors contributing to the determination of this growth rate. The pressure on resources and the environment is mounting, the economy is still hampered by a number of shortages, and there are still some unstable factors and uncertainties in development. It would therefore be inappropriate to set a higher growth rate. However, based on the need to increase our overall national strength, expand employment and alleviate social conflicts and considering the rapid economic growth we have had in recent years, it would also be inappropriate to set it too low. The target of around 8% is for China's overall economic growth. All localities should set reasonable and appropriate targets based on their conditions, avoid recklessly pursuing and competing for the highest growth rate, and put the main thrust of their effort into improving the quality and benefits of economic growth.
- Creation of 9 million new jobs for urban residents and confining the registered urban unemployment rate to 4.6%. Employment pressure will remain intense this year, and continued reform and restructuring of enterprises will make it difficult to increase employment over the short term. Estimates based on the relationship between economic growth and job creation indicate that by implementing a vigorous employment policy and gradually improving it, we can attain this target, though it will require a great deal of work.
- Rise in the consumer price index within 3%. This figure was set slightly higher than the actual rise last year based on several major factors. The high oil price on the international market will raise prices of oil-dependent products in the domestic market. Balancing price relationships among resource products, correcting certain irrational prices and raising prices for some services will drive up the consumer price index somewhat.
- Increase in the total import and export volume of 15%. We need to maintain a steady increase in import and export volumes. Given that the volume of exports is already rather high and the added value of many export commodities is very low, we should not set too high a target for foreign trade growth in order to help guide all parties concerned to change the way they increase foreign trade, to accelerate improvement of the import and export mix, and to maintain the equilibrium in balance of payments.
- Reduction of energy consumption per unit of GDP of about 4%. China is still in a period of fairly high consumption of resources, and it will take a while for measures to effectively increase energy savings and reduce material consumption to take hold. This will make it hard to meet the target. However, it would be difficult to continue pursuing growth based on inefficient energy consumption, and there is much room to increase energy savings and reduce consumption of materials. Thus, this target must and can be attained as long as we work even harder to restructure the economy and change the extensive pattern of economic growth as soon as possible.
- Steady increase in urban and rural incomes. The per capita disposable income of urban residents and the per capita net income of rural residents are expected to increase by 6% and 5% respectively in real terms. We arrived at these figures by taking several major factors into account. Rapid economic growth, continued improvement of the economic performance of enterprises, and gradual implementation of government measures to increase rural incomes and to strengthen social security and poverty alleviation work should all contribute to a steady increase in urban and rural incomes. However, there are quite a few difficulties that could slow the rise in personal incomes, particularly in rural incomes. Based on a steady increase in urban and rural incomes, consumer demand should continue to see steady and rapid growth this year, resulting in an expected 12% increase in retail sales of consumer goods nationwide.
- Faster development of science and technology, education and other social programs. We will strive to bring spending on R&D up to 1.45% of GDP. The secondary gross enrollment ratio should reach 57%, and plans call for enrolling 5.3 million undergraduate students and 400,000 graduate students in regular institutions of higher learning. The development of the system of public cultural services will be strengthened. The trial reform of a new type of rural cooperative medical care system will be expanded to about 40% of all counties (and county-level districts and cities) in China. The natural population growth rate should be confined below 7.5‰.
- Continued improvement of the natural environment. The total discharge of major pollutants will be reduced by 2%. We will increase the percentage of industrial solid waste that is comprehensively utilized to 56.2% and the percentage of urban sewage that is properly treated to 50%.
III. Principal Tasks and Measures for Economic and Social Development in 2006
To fulfill this year's targets for national economic and social development, we need to make unified planning and focus on key projects. We must keep the economy growing at a rapid yet steady pace, get off to a good start in building a new socialist countryside, make considerable progress in improving our capacity for independent innovation and in promoting economic restructuring, achieve significant reduction in energy and material consumption and progress in changing the pattern of economic growth, make breakthroughs in reforms of key areas, and make continued progress in building a harmonious socialist society. To achieve all this, we need to pay particular attention to the following ten aspects of our work.
1. We will keep macroeconomic policies stable and maintain rapid yet steady economic development. We will continue to follow prudent fiscal and monetary policies.
1) We need to cut the central budget deficit by an appropriate amount and continue to adjust the structure o
f expenditures. National revenue in the budget for 2006 totals 3.5423 trillion yuan, expenditures total 3.8373 trillion yuan, and the deficit in the central government budget is 295 billion yuan, 5 billion yuan less and a lower proportion of the GDP than last year. We will increase revenue and reduce expenditures, and strengthen collection and management of revenue in accordance with the law. Increases in common expenditures must be strictly held in check to ensure funding for key areas.
2) We need to reduce the issuance of long-term treasury bonds for development and make sure that bond funds are invested in the right areas. We plan to issue 60 billion yuan worth of long-term treasury bonds in 2006, 20 billion yuan less than last year, while increasing regular development investment from the central government budget by 10 billion yuan to 55.4 billion yuan. In accordance with the principle of cutting common expenditures to guarantee funding for key areas, we will continue to change the structure of expenditures financed by bond funds and budgetary allocations to ensure adequate funding for key projects already underway and to support an appropriate number of major new projects that have an overall impact on the implementation of the Eleventh Five-Year Development Guidelines. Investment from the central government will be used mainly to improve production and living conditions in rural areas and build a new socialist countryside; promote development of elementary education, public health and other social programs; support development of the western region and promote balanced development among regions; and support major infrastructure projects in environmental protection, ecological conservation, water conservancy, transportation and energy, and projects having a bearing on the safety of people's lives and property and affecting their vital interests. We will strengthen inspection and oversight of such projects and improve the returns of investment.
3) We need to maintain appropriate growth of the money supply and credit and optimize the structure of loan portfolios. The broad money supply (M2) and the narrow money supply (M1) are expected to increase by 16% and 14% respectively in 2006, and RMB loans totaling 2.5 trillion yuan will be granted. We will maintain the amount of intermediate and long-term loans at an appropriate level. We will guide financial institutions to grant more loans for working capital to enterprises that are profitable and make marketable products. We will work hard to solve the problem of farmers and small and medium-sized enterprises having difficulty obtaining loans. We will strengthen credit support for shoring up weak links in economic and social development, developing the western region, revitalizing Northeast China and other old industrial bases, and energizing the central region. We will develop direct financing and increase the issuance of enterprise bonds. We will continue to deregulate interest rates and make them more subject to market forces. We will improve the transmission mechanism for monetary policy. We need to improve the system of managed floating exchange rates to keep the RMB exchange rate basically stable at an appropriate and balanced level. We will continue to improve foreign exchange management, optimize the structure of state reserves, and strengthen monitoring of the capital flow into and out of the country.
4) We need to keep prices basically stable. We will continue to strengthen monitoring and analysis of the overall price level and price trends for important goods and services, such as grain, cotton, oil, coal, steel and commercial housing. We will do a good job in conducting roving inspections of prices.
We will strengthen regulation of fixed asset investment. Investment in fixed assets is expected to increase by 18% nationwide in 2006. We will continue to tighten oversight over the approval of land and credit to strictly control the number of new projects and curb the excessive growth in fixed asset investment to prevent a return to overheated investment. 1) We need to make the land management system as strict as possible to control conversion of rural land, especially cultivated land, to construction use. The total area of rural land converted to construction use will be limited to 266,700 hectares in 2006. 2) On the basis of the principle of handling each case on its own merits and expanding some industries while contracting others, we need to strictly control funding and land use for industries that have expanded too much to ensure all major state development projects and important projects in industrial restructuring have adequate land and funds. 3) We need to strengthen city planning, appropriately control the scale of housing demolition and standardize the use of bundled loans for urban development projects. We need to build on our achievements in clearing up problems relating to development zones and continue to improve related policies. 4) We need to restructure the availability of housing by increasing the supply of ordinary commercial housing and affordable housing while limiting high-end real estate projects, so that there is an appropriate mix of commercial housing, affordable housing and low-rent housing in the market. We will to basically clear up all overdue payments for construction projects and promote the sound development of the real estate and construction industries.
We will strive to expand consumption demand. 1) We will work hard to increase incomes of urban and rural residents, especially those in the lower- and middle-income brackets. We will appropriately raise basic pension benefits for retired enterprise employees, subsidies for various entitled groups such as disabled military personnel, and minimum living allowances for poor urban residents. We will make appropriate adjustments to the minimum pay standard for enterprise employees, enforce it strictly, and introduce a minimum hourly wage. We will reform the civil servant pay system in accordance with the Civil Service Law of the People's Republic of China. We will reform the income distribution system in institutions. 2) We need to improve consumer confidence. We will keep expected individual spending stable and stimulate immediate consumption by accelerating improvement in the social security system and solving outstanding problems in education, medical care, and housing. 3) We need to develop rural markets. We will accelerate the establishment of the wholesale and retail system in rural areas, and increase support for expansion of chain-store operations in the rural network of commerce and for the distribution of agricultural supplies. We will continue the project to encourage retailers to open stores in more townships and villages. We will develop community-based retail outlets and services in cities. 4) We need to develop new growth areas in consumption, encourage spending on cultural activities, fitness, tourism and other services, and standardize and develop the housing market and automobile market. 5) We need to improve the consumption environment and make appropriate adjustments to the consumption tax. We will accelerate development of a nationwide individual credit rating system and improve consumer credit policy. We will develop e-commerce. We will continue to review prices and charges for education and medicine and severely punish commercial fraud to protect the legitimate rights and interests of consumers.
We need to balance supply and demand in coal, electricity, oil, and transportation. We will keep the production and supply of coal stable without compromising production safety and develop large coalmining bases. We will speed up development of clean energy such as hydroelectric power, nuclear power and renewable energy sources, strive for optimal development of thermal power, and upgrade power grids. We will work hard to increase oil and natural gas supplies, carry out trial coal liquefaction projects and projects for developing and utilizing coal bed methane, and speed up the establishment of an oil conservation system. We will continue to strengthen development of coal transport facilities, embarkation ports and other major transportation infrastructure. We will develop a permanent mechanism for improving the demand-side management of electricity. We will do a good job coordinating coal, electricity, oil and transportation, focusing on solving problems with water, gas, electricity, heating and oil supplies that have a direct bearing on people's lives.
2. We will build a new socialist countryside, promote agricultural development and raise farmers' incomes. We will adhere to the principle of giving more, taking less and lessening control and accelerate the establishment of a permanent mechanism of getting industry to support agriculture and cities to support the countryside.
1) We need to steadily develop grain production. We will continue to improve the overall agricultural capacity and strive to maintain total grain output at last year's level. We will strengthen land management, protect primary farmland and stabilize the acreage sown to grain. We will step up development of large commercial grain bases and continue to implement the projects to industrialize production of high-quality grain crops, develop superior seed varieties and protect plants. We will increase transfer payments to major grain-producing counties and counties financially strapped. We will continue to set floor prices for the purchase of major grain varieties in short supply in major producing areas to keep market grain prices stable. We will also improve the system for controlling and using grain reserves to regulate grain prices at both national and provincial levels and ensure adequate local reserves.
2) We need to develop modern agriculture. We will concentrate the production of superior agricultural products in the most suitable areas and industrialize their production and management to meet the requirements for growing high-quality, high-yield crops that are cost-effective, eco-friendly and safe. We will speed up the development of agronomy and spread the use of advanced, applied technologies in agricultural production. We will develop a high-quality cotton production base in Xinjiang and an industrialized canola production belt in the Yangtze River basin. We will continue our projects for developing superior breeds of livestock, poultry and aquatic products, and encourage localities to develop intensive livestock, poultry or aquatic farming as appropriate for local conditions. We will quicken implementation of the program for preventing and controlling animal epidemics and fully implement measures supporting poultry farming.
3) We need to improve production and living conditions in the countryside. We are giving priority in infrastructure investment to rural areas to strengthen basic development of farmland, focusing on small water conservancy projects. We will support improvement of water conservation in large irrigated areas and upgrade of drainage pumping stations in the central region. We will pay close attention to developing infrastructure in areas such as water, methane, roads and electricity and improving people's living environment in rural areas. Investment from the central government budget for 2006 in safe drinking water projects in the countryside will double that of 2005, providing safe drinking water to another 20 million rural people who suffer from seasonal water shortages or whose water contains too much fluoride or arsenic or is brackish or contaminated. The central government will also increase its investment in rural methane facilities by 1.5-fold with the goal of building methane facilities to serve an additional 2.5 million rural families to encourage them to renovate their animal enclosures, toilets and kitchens. We will launch the rural road upgrade project under the Eleventh Five-Year Development Guidelines to extend asphalt or concrete roads to more villages in the eastern and central regions and to more townships in the western region. We will accelerate work to supply electricity to villages without power and upgrade some provinces' rural power grids.
4) We need to speed up development of public services in rural areas. All students receiving compulsory education in western rural areas will be exempted from tuition and miscellaneous fees this year. We will continue to provide free textbooks for poor rural students receiving compulsory education and living allowances for those boarding on campus. We will increase funding to support compulsory education at primary and secondary schools in rural areas, set up a sound funding mechanism for repairing and renovating rural primary and secondary school buildings, and improve the mechanism for guaranteeing payment of teachers' salaries at rural primary and secondary schools. We will basically complete the renovation of rural boarding schools and the project for modern distance learning at rural primary and secondary schools. We will carry out the program for establishing and developing a system of rural health care services, and accelerate the development of the rural health care infrastructure, concentrating on the central and western regions. We will build or renovate another 4,200 town and township hospitals, reaching 68% of the target in the program. We will extend the pilot projects for a new type of rural cooperative medical care system and implement a medical assistance system in rural areas. We will launch the project to extend radio and TV coverage to every village with electricity and 20 or more households, continue the project to screen movies in rural areas, and promote development of town and township cultural centers.
5) We need to increase rural incomes through a variety of channels. We will steadily move forward with industrialization of agricultural production and management, integrate agriculture with trade and industry, and develop a variety of specialized economic cooperatives and leading enterprises that process agricultural and sideline products so as to tap the potential within the agricultural sector for increasing incomes. We will increase direct subsidies to farmers for growing grain, subsidies for cultivating improved crop strains and subsidies for purchasing agricultural machinery and tools, and phase in a system of direct subsidies to grain producers for purchasing agricultural supplies, such as fertilizers and diesel fuel. We will tighten oversight and management of fertilizer prices and agriculture-related charges, curb price increases for agricultural supplies and lessen farmers' burdens. We will encourage rural laborers to enter the urban workforce and find non-agricultural employment by improving vocational training for rural migrant workers, canceling discriminatory policies against them, and adopting measures to ensure their wages are paid on time and in full. We will boost economic development in counties.
3. We will enhance capacity for independent innovation and build an innovation-oriented country. We will carry out the Outline of the National Long- and Medium-Term Program for Scientific and Technological Development (2006-2020) and promote original innovation, integrated innovation and improvement of imported technologies through digestion and absorption.
1) We need to work harder to tackle key problems in science and technology. When proper conditions are in place, we will launch major science and technology projects such as those to develop important new medicines and genetically modified organisms. We will carry out major scientific research programs in such areas as protein technology and nanotechnology. We will concentrate our strength to tackle pivotal technological problems in major industries such as energy, resources, information and equipment. We will intensify research on technologies for public welfare concerning ecological issues, population, health care and public security. We will continue to encourage philosophy and the social sciences to flourish.
2) We need to speed up development of the national innovation system. We will strengthen the role of enterprises to make them the main source of independent innovation, and build up technology centers in about 3,000 leading enterprises in various industries. We will set up a number of national engineering centers to improve control of coalmine gas, develop new vaccines and build ships, and establish a number of national laboratories in fields such as next-generation Internet and biometallurgy. We will carry out nine major science and technology infrastructure projects, including those to develop a general-purpose oceanographic research vessel and next-generation large astronomical telescopes. We will start the third phase of the Knowledge Innovation Program in the Chinese Academy of Sciences. We will improve the national system for science and technology planning to optimize allocation of science and technology resources and promote the industrial application of advances in science and technology. We will encourage research institutes engaged in technology development to become enterprises and promote the reform of public service research institutes. We will improve the system of scientific and technological review and accreditation and the system for assessing and rewarding advances in science and technology. We will develop intermediary services for science and technology. We will make more efforts to disseminate knowledge about science and technology among the public, and implement the Action Plan to Increase the Population's Understanding of Science.
3) We need to put more details about fiscal support, taxation, financing and government procurement in the preferential policies for independent innovation and encourage enterprises to invest more in R&D. We will support introduction of major technologies through joint bidding by a consortium of end-users, manufacturing enterprises and design institutes. We will set up a mechanism to ensure stable growth of government investment in scientific research and a fund for guiding venture capital investment. We will give policy support for preferential use of equipment that is newly developed and manufactured domestically and tighten supervision over the import of major technologies and equipment to avoid haphazard decision-making and duplication. We will help small and medium-sized enterprises to improve their capacity for independent innovation and encourage foreign enterprises to locate R&D activities in China. We will strengthen protection of intellectual property rights.
4) We need to step up human resources development in science and technology. We will set up a sound personnel evaluation system. We will cultivate a group of scientific project managers through development of key state projects, leading scholars through development of key disciplines, and strategic scientists through development of major research institutes.
4. We will accelerate optimization and upgrading of the industrial structure and enhance the technological level and overall competitiveness of industries.
1) We will vigorously carry out restructuring of some industries with surplus production capacity. We will combine economic, legal and necessary administrative measures and make full use of market forces to help superior enterprises prosper and allow inferior ones to perish. We will effectively guide industrial development through industrial policy, regulate it through credit policy and support it through fiscal policy. We will continue to improve industrial planning; implement the Provisional Measures for Promoting Industrial Restructuring; raise and enforce market access requirements concerning environmental protection, safety, technology, land and the comprehensive use of resources; and strictly control the expansion of production capacity. We will continue to screen projects under construction or planned for construction and stop those that do not meet the requirements for market access through legal means. We will close a number of enterprises that waste resources, pollute the environment or do not have the conditions to ensure production safety in accordance with the law. We will transform and upgrade traditional industries, focusing on improving technologies, making better products, protecting the environment, decreasing the consumption of energy and materials, and improving production safety. We will encourage merger and reorganization in the steel, cement, electrolytic aluminum and coal industries on the basis of market principles, support the efforts of competitive enterprises to grow stronger and larger, and raise the overall technological level and concentration of industries.
2) We will accelerate the development of high-tech industries. We will improve credit services and the financing environment for high-tech enterprises. Focusing on such key industries as integrated circuits, software, and new components, we will foster a group of IT industries, such as digital AV equipment, next-generation Internet, next-generation mobile communications, high performance computers and network equipment. We will vigorously develop the biotechnology industry. We will accelerate the projects to develop radio and television broadcasting satellites and new feeder aircrafts. We will continue to use IT to drive industrialization and make wide use of new and high technology and cutting-edge applied technology to upgrade traditional industries.
3) We will revitalize the equipment manufacturing industry. We will improve policies and measures for supporting the development of major equipment. We will accelerate the domestic production of essential equipment through the development of major projects in 16 key areas, including gas-driven turbines, super-critical and ultra-supercritical coal-fired power generating units, mega kilowatt nuclear power generators, high-speed trains, and large, complete coal conversion facilities, and consequently stimulate the development of basic products and parts.
4) We will promote overall development of the service sector. We will carry out reform and innovation in the system of service industries in a number of cities on a trial basis. We will accelerate the development of service industries that support production, such as transportation, banking, information, modern logistics and all kinds of intermediary services, and the development of emerging consumer service industries, such as community services and tourism. We will improve the quality of service in traditional service industries, such as commerce and trade, food and beverage services, and postal service.
5. We will strengthen resource conservation and environmental protection and promote transformation of the pattern of economic growth.
1) We will promote energy conservation and lower resource consumption. We will promptly formulate new and improve existing standards for all industries to conserve energy, water, materials and land, and establish a system for verifying whether all localities and major industries meet their targets for energy consumption and a system for publishing energy consumption per unit of GDP. We will implement ten major energy conservation projects, concentrating on improving energy conservation in 1,000 enterprises with high energy consumption. We will expand the scope of certification of energy-conserving products, apply compulsory energy efficiency standards, and strengthen supervision of the use of energy efficiency labeling on key energy-consuming products. We will continue to encourage government departments to buy and use energy-conserving products. We will develop water-efficient irrigation. We will help industries with high water consumption to adopt water-conserving technology, accelerate the construction of water-recycling facilities, support the desalination and direct use of seawater, and spread the application of water-conserving equipment and tools. We will strengthen supervision of raw material consumption in key industries. We will encourage the development of high-strength, corrosion-resistant metal materials and promote the conservation of lumber and the use of wood substitutes. We will intensify the conservation and intensive use of land, set sound quotas for how much land can be given over to construction projects, and develop buildings that conserve energy and land. We will institute a deadline in a second group of cities for banning the use of solid clay bricks.
2) We will develop a circular economy. We will improve fiscal, tax and pricing policies to promote the development of a circular economy and the conservation and comprehensive use of resources. We will carry out state pilot projects for a circular economy. We will support R&D on key and general technologies for the circular economy and the demonstration projects for their industrial application. We will promote the comprehensive utilization of associated minerals and industrial waste and the recycling of renewable resources. We will broadly undertake publicity and education to promote consumption patterns and lifestyles that are healthy, civilized and resource conserving.
3) We will do a good job of ecological conservation and environmental protection. We will continue to carry out key ecological projects, such as those to protect virgin forests, conserve water and soil, bring the sources of dust storms affecting Beijing and Tianjin under control, protect and improve the ecology of the Sanjiangyuan Nature Preserve, and build a greenbelt around the Three Gorges Reservoir. We will promptly set up the mechanism for ecological compensation. We will intensify efforts to prevent and control pollution in the key watersheds of the Huai, Hai and Liao rivers, Tai, Chao and Dianchi lakes, the Bohai Sea region, the Three Gorges Reservoir area and along the routes of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. We must strictly protect urban potable water sources. We will strengthen the control of sulfur dioxide emissions from coal-fired power plants. We will take comprehensive measures to prevent and control air pollution in cities. We will promote clean production. We will improve oversight and management of nuclear safety and radioactive environments. We will conscientiously implement the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. We will develop environment-friendly industries.
6. We will make full use of comparative advantages to promote balanced development among regions.
1) We will promote the development of key areas, cities and industries in the western region and strengthen the region's capability for self-development. We will launch a number of major infrastructure projects. We will consolidate and build on our achievements in returning farmland to forests and grazing land to grassland. We will continue to control water pollution in the upper reaches of the Yangtze and Yellow rivers. We will make greater efforts to prospect for and exploit mineral resources and support the development of oil refineries and centers for processing rare earth elements, potash and phosphate fertilizers, and other locally distinctive resources. We will further strengthen science and technology, education, human resources development and the legal system in the western region. We will accelerate establishment of permanent, stable channels to fund development of the region.
2) In the northeast, we will intensify development of large grain production bases and promote restructuring in key industries and reform and reorganization of state-owned enterprises. We will do a good job in transforming the economies of cities reliant on resource industries, in bringing sinkholes in coalmining areas under control and in renovating shantytowns. We will carry out ecological improvement projects, focusing on the Songhua and Liao river valleys. We will promptly work out mechanisms for compensating for resource depletion and for assisting declining industries. We will carry out a trial reform of collectively owned enterprises operated by state-owned enterprises in the northeast. We will conscientiously implement policy measures to open up further both domestically and internationally.
3) We will work out and implement gu
idelines for energizing the central region by increasing support for industrial development, major infrastructure projects, investment, and the effort to promote reform and opening up. We will focus on developing modern agriculture, particularly commercial grain bases in main grain-producing areas, bases for producing energy and important raw materials, centers for modern equipment manufacturing and high-tech industries, and a comprehensive transportation system. We will develop a modern wholesale and retailer industry. We will help old industrial cities to accelerate reorganization and upgrading of their enterprises and cities reliant on resource industries to transform their economies. We will strengthen the role of major cities in stimulating the development of surrounding areas.
4) The eastern region should take the lead in increasing international competitiveness and capacity for independent innovation and sustainable development. It should place greater emphasis on conserving land, water, energy and mineral resources and accelerate development of high-tech industries and modern service industries. We will continue to make the most of special economic zones and the Pudong New Area in Shanghai and promote development and opening up of the Binhai New Area in Tianjin. We will support economic development on the west shore of the Taiwan Straits and in other areas where Taiwan investment is concentrated. We will vigorously develop the marine economy.
5) We will increase support for the economic and social development of old revolutionary areas, ethnic minority regions, border areas and poor areas. We will give more aid to ethnic groups with small populations and continue working to vitalize border areas and enrich the people living there. We will improve the mechanism whereby economically better off areas assist underdeveloped areas in development, and continue to promote regional cooperation and encourage stronger localities to help weaker ones.
6) We will begin studies on development priority zoning, appropriately identifying four types of zones, i.e., optimal development zones, key development zones, restricted development zones and non-development zones; and set objectives for development and supporting policies on the basis of their zoning.
7. We will continue to deepen reform and create an institutional environment for scientific development. We will strengthen overall guidance, coordinated planning and comprehensive support for reforms and continue to make breakthroughs in a number of important areas.
1) We will comprehensively advance overall rural reform, focusing on town and township administrative bodies, rural compulsory education, and the fiscal management systems at county and township levels. We will standardize policies for transferring rural land and accelerate reform of the rural land expropriation system. We will deepen reform of the grain and cotton distribution systems. We will improve the system of rural credit cooperatives; reform the Agricultural Bank of China and the Agricultural Development Bank of China; conduct trials of policy-based agricultural insurance; and improve financial services in rural areas.
2) We will deepen enterprise reform. Taking advantage of the implementation of the revised Company Law, we will transform large state-owned enterprises into joint stock companies, and improve the property ownership structure, corporate governance, and incentive and restraint mechanisms. We will accelerate formation of a number of large companies and enterprise groups that have their own intellectual property rights and famous brands and are internationally competitive. We will continue to carry out policy-based closures and bankruptcies of enterprises, relieve enterprises from the burden of operating social programs and spin off their auxiliary businesses from their main business. We will standardize procedures for transforming stated-owned enterprises and for transferring state-owned property rights to prevent the loss of state assets and safeguard the lawful rights and interests of workers. We will accelerate the establishment of a budget system for managing state capital and set up a sound system for overseeing and managing non-productive assets and natural resource assets. We will deepen reform of the systems for managing telecommunications, electricity, civil aviation, the postal service and tobacco. We will continue to reform the railroad investment and financing system and work out a plan for restructuring the railroad industry. We will deepen reform of urban public utilities such as water, gas and heating supplies by giving greater play to market forces and improving market supervision. We will promote the reform and development of collectively owned enterprises. We will improve the policy measures for encouraging, supporting and guiding the development of the non-public sector of the economy, and carry out the project to nurture small and mid-sized enterprises.
3) We will accelerate reform of the financial system. We will continue the reform to introduce the joint stock system in state-owned commercial banks while retaining a majority of the stock in the hands of the state and improve the corporate governance and internal management system of these banks. We will promote vigorous yet steady reform and development of the capital market, improve the quality of listed companies, do a good job in overall regulation of securities brokerage companies, and continue to carry out reform of the shareholder structure and trials of an industrial investment fund. We will deepen reform of the insurance industry and carry out reforms of policy banks, postal savings institutions and other financial institutions. We will standardize financial markets, improve financial oversight and supervision, safeguard financial stability and security, and guard against and defuse financial risks.
4) We will deepen reform of the fiscal and tax systems. We will improve the public finance system and the transfer payment system, reform the classification of government revenue and expenditures, and improve the budget management system. We will vigorously carry out VAT reform, improve the resource tax, and work out a unified tax collection system coving all types of enterprises.
5) We will deepen reform of the investment system. We will improve the system for approving and recording investment projects. We will promptly formulate measures for supervising investment directly from the central budget and for assigning accountability for bad decisions on projects financed by the central government. We will improve the mechanism for macro-control of investment.
6) We will carry out vigorous but steady price reform for resource products. We will continue to charge different prices for electricity at peak and off-peak hours, steadily promote public bidding for the right to supply electricity, and implement an electricity pricing mechanism that encourages the development of renewable energy resources. We will improve the mechanism for setting oil prices. We will adjust the producer price for natural gas. We will expand the collection of fees for water resources, rationally adjust prices for urban water supplies and for water from water conservancy projects, charge fees for sewage treatment in all cities, and implement progressive pricing and apply surcharges for water used in excess of quotas in areas where conditions permit. We will establish a standardized system of base land prices. In pricing reform, we need to consider the interests of all parties and adopt special measures to ensure that the basic living standard of low-income people is not affected.
7) We will carry out reform of the administrative system. We will fully implement the Administrative Permission Law, transform government functions, reduce the number of matters requiring administrative approval and standardize approval procedures. We will improve the system of consultation and coordination of decision making on important matters that have a bearing on the overall economic and social development. We will improve the system of expert appraisal, technical consultation and decision evaluation and the system of public notices and hearings in order to make decision making more scientific and democratic. We will press ahead with the reform of institutions.
8. We will implement an open, win-win strategy to improve the quality and level of China's opening to the outside world.
1) Transformation of the pattern of foreign trade growth needs to be accelerated, and the import and export mix needs to be optimized. We will vigorously implement the strategy of stimulating foreign trade through science and technology. We will improve tax rebate measures, financial support measures, and brand certification measures to raise the overall quality, grade and added value of export products. We will help enterprises expand exports of new and high technology and electromechanical products for which they possess the intellectual property and trademark rights. We will promote transformation and upgrading of the processing trade to shift processing to more sophisticated operations and more intensively processed products. We will control the export of highly polluting products, resource products and products that consume excessive quantities of energy. We will increase imports mainly in the areas of advanced technologies, key equipment, and resources in short supply in China and strive to redress the trade imbalance. We will do a good job in the work after the transition period following China's accession to the WTO. We will strengthen regional, multilateral and bilateral economic and trade cooperation. We will further implement the measures of the Closer Economic Partnership Arrangement the mainland has with Hong Kong and Macao.
2) We will continue to make effective use of foreign investment, optimize the structure and improve its performance. We will encourage multinational corporations to transfer processing and manufacturing operations with high value-added and high-tech content to China, to outsource services to China and to set up R&D facilities here. In order to protect our industries, we will guide foreign investment toward certain industries and regions, improve and standardize policies related to corporate takeovers, and strictly control the entry of low-level foreign-funded projects that consume large quantities of energy and resources or cause serious pollution.
3) We must actively yet steadily follow the go global strategy. We will continue to support and guide overseas investment by qualified enterprises, improve policies, laws and regulations and systems for stimulating and guaranteeing overseas investment, and strengthen the coordination and oversight mechanism.
9. We will continue to make education a high strategic priority in development and promote all-round progress of social programs.
1) Development of education is a high priority. We will extensively promote competence-oriented education. We will make nine-year compulsory education more widely available and consolidate past progress, and we will place greater responsibility on government for guaranteeing compulsory education. We will also improve conditions in rural schools and solve the problems that low-income urban families and rural migrant workers in cities have in sending their children to school. We will launch a project to improve the infrastructure of vocational education, and earmark special funds for building county vocational education centers, secondary vocational schools and demonstration vocational colleges. We will promote the balanced development of high schools. We will continue to implement the 211 Project and the May 1998 Program to improve the quality of higher education. We will encourage the development of schools run by the non-state sector.
2) We will improve the public health and basic medical care systems. We will complete the establishment of a medical treatment system for public health emergencies. We will optimize distribution of urban medical care resources and build a new type of community-based medical and health care system. We will continue to do a good job of preventing and controlling major diseases such as AIDS, tuberculosis, snail fever and the highly pathogenic avian influenza. We will promote the reforms of the medical and health care system and the pharmaceutical production and distribution system. We will continue to reduce drug prices, rectify market prices of medical equipment, improve medical ethics and practices, standardize the diagnosis and treatment of diseases and the prescribing of drugs, and solve the problem of inadequate and unaffordable medical care. We will support development of traditional Chinese medicine.
3) We will energetically develop culture, radio, TV, film, the press, publishing, tourism and sports. We will deepen reform of the cultural system. We will promote the construction of cultural facilities and intensify protection of major natural and cultural heritage sites and folk culture. We will do our work related to the press and publishing well. We will intensify infrastructure development for well-known scenic sites and related sites, focusing efforts on major red tourism attractions and popular scenic routes throughout the country. We will promote fitness programs for the general public and raise the level of competitive sports. We will continue to do a good job preparing for the 2008 Olympic Games in Beijing and the 2010 World Exposition in Shanghai.
4) We will continue the current family planning policy, keep the low birthrate stable, and improve the overall quality of newborns. We need to improve the family planning service network at the lower levels, focusing on the development of family planning facilities in counties and key townships in the central and western regions. We will also improve family planning management and services for the floating population. We will expand the coverage of the system for rewarding and assisting rural families that observe the family planning policy and the scope of the “Fewer Children Equals Faster Prosperity Project” in the western region. We will energetically develop programs for the elderly.
10. We will conscientiously work to resolve problems that affect the vital interests of the people and pay very close attention to safeguarding social stability. We will promote the building of a harmonious society, focusing on increasing employment, improving the social security system, distributing wealth more equitably and safeguarding social stability.
1) We will continue to follow a vigorous employment policy. We will take more steps to help people laid off because of economic restructuring find new jobs and make appropriate arrangements for employees of state-owned enterprises that have been reorganized and restructured, or closed and declared bankrupt. We will energetically develop service industries, labor-intensive industries and small and medium-sized enterprises to provide more employment opportunities. We will do a good job in providing guidance and services for people newly entering the workforce, particularly college graduates, demobilized soldiers and people having difficulty finding jobs. We will provide more vocational training and energetically develop the system of employment services. We will improve the system for helping people with special difficulties find employment. We will encourage more people to find jobs for themselves or start their own businesses and support various forms of flexible employment. We will strengthen protection of the rights and interests of workers.
2) We will speed up development of the social security system. We will ensure that all social security benefits are paid on time. We will continue to expand the coverage of the social security system in urban areas. We will improve the basic old-age insurance and basic medical insurance systems in counties and towns and turn over their management to higher-level authorities. We will do a good job of providing minimum living allowances for poor urban residents. We will set up a system for providing minimum living allowances to poor rural residents in localities where conditions permit. We will improve the systems for unemployment insurance, worker's compensation and maternity insurance. We will actively yet steadily work to resolve the problem of inadequate social safety net for rural migrant workers and farmers whose land has been expropriated. We will promptly set up a welfare system for destitute urban and rural residents. We will develop programs to help the disabled and support social-benefit and charity undertakings.
3) We will make appropriate adjustments in income distribution. We will promptly set up a monitoring and early warning system for income distribution. We will standardize order in income distribution, raise taxes on high-income earners, and improve the system of norms and oversight for income distribution in state-owned enterprises and institutions. We will improve the collection and management of the individual income tax and suppress all types of illegal income.
4) We will help needy urban and rural residents in their work and lives. We will step up efforts to reduce poverty through development, and we will steadily carry out pilot programs to give people work instead of relief subsidies and to relocate people from inhospitable areas. We will do a good job in providing relief, restoring production, and rebuilding in disaster-hit areas. We will improve the system for providing food, clothing, medical care, housing and burial expenses for childless and infirm rural residents, the system for providing assistance to rural families in extreme poverty and the system for providing relief to disaster victims by increasing financial support and appropriately raising the level of assistance.
5) We will further strengthen production safety management. The responsibility system for production safety will be strictly implemented, and factories and mines that do not have the conditions to ensure safe production will be closed in accordance with the law. We will improve production safety in key areas such as mines, transportation, hazardous chemicals and fireworks. We will intensify oversight to ensure the quality and safety of foodstuffs and medicines and proper sanitary conditions in the food and beverage industry. It is especially important that we allocate more funds for upgrading safety technologies and improving gas control in coalmines on the principle of enterprises taking responsibility and government providing support. In other words, coalmines must make good use of funding for production safety, the central government will continue to provide funding and local governments should increase their financial support. By using these funds to improve safety systems for ventilation, dust management, fire prevention, water removal and coal transport, and to improve extraction and comprehensive utilization of gas, we will firmly put a stop to the increasing occurrence of catastrophic incidents.
6) We will safeguard and promote social stability. We will focus on solving problems that harm the interests of people, such as those concerning land expropriation, housing demolition and resident relocation, enterprise restructuring, displacement of people from reservoir areas and environmental pollution. We will improve the early warning system for disturbances to social stability and the emergency response mechanism so that we can properly respond to natural disasters, catastrophic accidents, public health emergencies and other emergency situations that threaten public security. We will improve the system for safeguarding public security through prevention and control and increase efforts to develop harmonious communities, villages and towns in order to create a social environment in both urban and rural areas where people can live and work in peace and happiness.
Our tasks in reform, development and stability for 2006 are arduous. Under the leadership of the Party Central Committee with Comrade Hu Jintao as General Secretary, we will hold high the great banner of Deng Xiaoping Theory and the important thought of Three Represents, fully implement a scientific outlook on development, and work hard with one heart and one mind in a down-to-earth manner to achieve the targets for economic and social development and get the Eleventh Five-Year Development Guidelines off to a good start!
(China.org.cn March 16, 2006)
|





