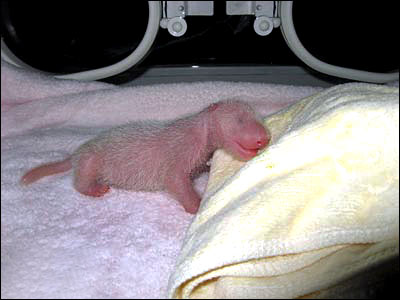
In 1990, the world's first panda twins survived.
At night, the giant panda nursery is calm and quiet.
Through the rhythm of the autumn rain, the sound of cubs suckling emerges. Five giant panda mothers, Qi Yuan, Cheng Ji, Er Ya Tou, Shu Qing and Bing Bing, are sleeping, eating bamboo, or nursing their babies in their own "suites" and enjoying the happiness of motherhood.
However, the personnel on duty are rather busy. They have to help the giant panda cubs to excrete waste and feed them with milk every four hours. They have to weigh the panda babies, take their temperatures, and keep records on the conditions of the mothers and their cubs.
In 2007 the Chengdu Research Base for Giant Panda Breeding (CRBGPB) brought good news from its delivery rooms: 5 giant pandas gave birth to 9 babies. This was a very meaningful gift for the 20th anniversary of the CRBGPB. Over the last twenty years the CRBGPB has successfully bred 110 babies for 82 giant panda mothers. Currently 68 giant pandas of four generations live on this base as part of the world's largest artificial breeding species.
The United Nations awarded the CRBGPB with the "global 500" environmental award twice, and more importantly, Chengdu has set a successful example for the Ex Situ Conservation for the endangered giant pandas.
The lightest 51g panda baby survived.
Two disasters
According to the standard set by the IUCN, Ex Situ Conservation is required when the number of an endangered species is less than 1,000. At this point, experts should interfere and create a man-made environment, such as a zoo, to prevent it from extinction.
The Futou Mountain on the northern outskirts of Chengdu was turned into a giant panda Ex Situ Conservation site due in part to two disasters.
From 1974 to 1976 the giant pandas suffered through famine. The Chengdu Zoo sent Zhang Anju to join an investigation group organized by the State Forestry Administration to investigate the situation on Minshan Mountain. The investigators found a total of 138 giant pandas scattered around the mountains and forests, with some dead bodies torn apart by scavengers and others curled up in the snow trying to protect their cubs. The tragic scene brought tears to the eyes of even the toughest among them.
Many ill and malnourished giant pandas were sent to the Chengdu Zoo for treatment. All of them were very skinny, infected with ringworms, and some were too weak to bite food.
In the summer of 1983 another calamity struck this area. Arrow bamboo around Minshan Mountain and Qionglai Mountain withered due to the natural cycle of blooming, affecting more than 500 pandas.
Chengdu Zoo once again became the medical treatment center for the giant pandas. About 90 percent of the giant pandas sent to the Chengdu Zoo were saved, but since the ecological conditions had not yet been restored in their natural habitat, recovered giant pandas couldn't be released to the mountains and forests. From this emerged the Ex Situ Conservation strategic thought.
During the Spring Festival of 1986, Zhang Anju, who became director of the Chengdu Gardening and Forestry Bureau, Zheng Shuling of the Ministry of Construction, and Hu Tieqing, Director of the Forestry Department of Sichuan Province reached a consensus that a "base" should be built. The base, later named the Chengdu Research Base for Giant Panda Breeding, would not only be a "breeding place" but also a research institute for studying the giant panda.
Determined not to let the pandas suffer, they built houses and planted trees, and soon large areas of bamboo spread around the mountain and created a simulated habitat for the giant pandas.
The phase I project was miraculously finished in one year.
Difficulties confronting artificial breeding
The success of Ex Situ Conservation depends on whether the species whose living conditions have been changed could multiply generation after generation.
In the early 1980s, one Beijing expert asserted that it was difficult to artificially breed giant pandas. The difficulties range from getting them inseminated, getting them pregnant to raising their cubs.
Two experts, He Guangxin and Li Guanghan, told the Southern Weekend in detail how the base solved these difficulties.
Man-reared female giant pandas could raise their rate of pregnancy if they combined natural intercourse with artificial insemination. In the early 1980s, the technological personnel of the Chengdu zoo began to study the collection of frozen semen. They found that it was later difficult to activate the sperm. In order to solve this problem, the base learned various techniques and even communicated with the American experts. Due to their painstaking efforts, they finally solved this problem.
Currently the survival rate of the sperm in the frozen semen reaches 90 percent and the sperm can be preserved for more than 100 years.
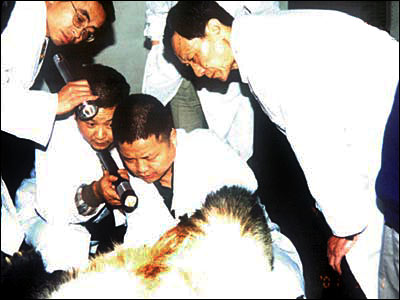
Researchers conducting artificial insemination of a giant panda
1990: a blissful year for panda breeding
Before the year 1990, the survival rate of captive-bred cubs was merely 33 percent. That is largely because twin cubs are commonplace in delivery and in the wild the mother panda usually abandons one and picks one to feed. Therefore, the postnatal nursing work is a key factor to raising the survival rate of the newborns.
In September 1963, the first captive-bred panda was born at the Beijing Zoo. He Guangxin was there as a zookeeper that day and recalled they kept the pandas in intensive care but only touched them during feeding for fear of disturbing maternal care.
Later they developed a method to keep the mother calm while approaching her cub. This finding made it possible to take the abandoned cub away while she nursed the other, but they were uncertain about how to maintain body temperature and synthesize milk for supplementary care.
In 1988, Mei Mei gave birth to two cubs. The zookeepers wrapped them in towels and warmed them by holding them firmly. The body temperature was around 36 to 37 degree Celsius by measurement. This temperature guideline was later applied to the automatic incubator.
Determining the type of milk to use was much more difficult. They tried almost all kinds of milk formulas ranging from cow milk to goat milk, and eventually human milk. However, none of these managed to save the cub's life. Japanese scientists had even attempted to formulate artificial milk, but a vital antibody needed was too complicated to be synthesized.
The keepers in the base finally figured out a way to make the mother feed both of the siblings alternately while thinking there was only one cub. Such an attempt was risky, but worthwhile. In 1989, the veterinarian Zhong Shunlong and other caretakers attempted the switch but it resulted in tragedy as the mother Mei Mei went on a rampage and pounced on her babies, causing their immediate death.
In 1990, Qing Qing gave birth to twin cubs. Even though it has previously ended in disaster, they still decided to try the "trickery" again, because only in this way could the two cubs survive. The breeder took one of the twins away by obstructing the mother's view and then brought it back after the unwitting mother had breast-fed her other baby. This time the twins successfully got breast-fed alternately, and coupled with other nutritious supplements, the siblings were in good health.
The base made the experience gained in breeding twin cubs known to the public and found wider applications. Generous Qing Qing not only breast-fed her own cubs, but aided other mother pandas. The mother panda Ya Ya also came to help other inexperienced mothers feed their cubs.
Panda town in the making
The base is also a talent pool, with many brilliant minds joining the team.
"I am happy that a group of talents such as Dr. Zhang Zhihe work at the base," Zhang Anju said, brimming with joy. These young scientists contribute to the base in one way or another, and over 20 years, they have churned out a host of research achievements and scholarly writings.
Zhang Anju in collaboration with a British biologist published a book that took ten years to complete, culling 90 papers from experts both domestically and internationally, 16 of which were written by the base researchers.
Dr. Zhang Zhihe and Wei Fuwen brought out a book on protection of the panda reserve. Zhao Ermi, a renowned biologist paid a tribute to the book, saying: "The book offers a synopsis on the protective work done in the panda reserve, and also is a good meld of new theories and technologies."
A plan is underway to construct a "panda town" as a spin-off to diversify the function of the base that has achieved milestone work in protecting pandas.
Zhang Zhihe, now Director of the base, said: "There are about 200 pandas living in captivity at present. When the number climbs to around 300, some of them can be released to the natural habitats, contributing to a comeback for the endangered species."
(China.org.cn by Zhang Ming'ai and He Shan, November 26, 2007)