Doing Business in beijing I . Survey
(i) Geography
The urban area of Beijing, located at 39?㼯span>N and 116 ?ㅠ, is bound by the mountains to the west, north and north-east and opens to the North China Plain, which falls away to the Bohai Sea in the east. The altitude of the plain Beijing lies on ranges from 20m to 60m, while the mountains average from 1,000m to 1,500m in hight. Mount Dongling, on the border with Heibei Province, is the municipality's highest point, with an altitude of 2,303 m. The major rivers flowing through the municipality are the Chaobai River and Beiyun River in the east and Yongding River and Juma River in the west. The urban areas of the city are divided into Dongcheng, Xicheng, Chongwen, Xuanwu, Chaoyang, Haidian, Fengtai and Shijingshan districts, and the rural areas are comprised of Mentougou, Fangshan, Tongzhou, Shunyi, Changping, Daxing, Pinggu and Huairou districts and Miyun and Yangqing counties. The municipality covers an area of 16,410.54 km2 with an urban area of 1,368.32 km2 and a rural area of 15,042.22 km2.
(ii) Climate
The city is of temperate continental climate, characterized by hot, humid summers, cold, dry winters and short springs and autumns. The average annual temperature is 10 to 12?样ith a lowest and highest recorded temperature of -27.4?校nd 42?栲espectively. The city is one of the rainiest regions in the northern part of China with an annual precipitation of over 600 mm, 75% of which falls in the summer months.
(iii) Population and Nationalities
The population of Beijing Municipality, defined as the total number of people who reside in the city for six or more months of the year, was 15.38 million in 2005. Of these, 11.870 million had a Bei jing permanent residence certificate. Among those with permanent residence status, 3.005 million worked in the agricultural sector. The density of the population is 937.2 per square km. Religions practiced by residents include Buddhism, Taoism, Islam and Christianity. Among the 56 ethnic groups in the city, those numbering over 10,000 include Hui, Manchu and Mongolian; those numbering over 1,000 include Zhuang, Uygur, Tujia and Tibetan.
(iv) Transportation and Infrastructure
Transportation
Beijing is a significant transportation hub in China.
The streets of Beijing are laid out like a chessboard. The Second, Third, Fourth and Fifth ring roads, connecting with many other main routes, constitute a complete urban roads system. There are 12 National Highways and nine expressways radiating from Beijing in all directions. In 2005, the subway line in Beijing reached 114km. Construction of the No.5, No.10 first stage (including the Olympic link) and the No.4 subway lines and an express rail link to the airport is well under way. Total road length in the municipality is 4,696 km, with 548 km of expressways. By 2005, on 14,713 km of roads in Beijing, 300.5 million tons of cargo and 519.25 million passengers are transported accounting for 92.4% and 85.3% of the total respectively.
Beijing is a railway hub of the People's Republic of China. There are several major railways radiating out from Beijing, including those to Guangzhou, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Baotou (in Inner Mongolia) and Qinhuangdao (in Hebei). China's rail network covers 30 provinces, municipalities and autonomous regions as well as Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. By 2005, Beijing's railway transportation lines were 964.4 km long with a cargo transportation capacity of 197.62 tons, accounting for 6.1% of the total and passenger transportation capacity of 57.78 million, constituting 9.5% of the total.
Beijing Capital International Airport is the busiest of China's international airports. Its network covers all China's provinces, municipalities, autonomous regions, Hong Kong and Macau, as well as 54 cities in 39 countries around the world. In 2005, the total amount of air cargo into and out of Beijing Capital International Airport reached 769,000 tons. Air passenger transportation amounted to 31.36 million passengers, constituting 5.2% of the total.
Post and telecommunications
The postal services to and from all countries and regions around the world are available in Beijing. The telephone network connects 2,300 domestic cities and 260 foreign countries and regions. In 2005, the total revenue of post and telecommunication services reached 41.75 billion yuan with 3.35 billion yuan from post services and 38.4 billion yuan from telecommunication services.The number of subscribers amounted to 9.5million, among those 8.545 million were in urban areas and 0.955 million were in rural areas. Cell phone users reached 147 million in Beijing, which means that 97 out every 100 people own a cell phone.
Finance and insurance
The financial industryp lays a significant role in Beijing's economy. In 2005, the financial assets in Beijing totaled 14.1 trillion yuan, with an added value of 79.28 billion yuan in the financial sector. Under a relatively sound financial organization system, branches of financial institutions in the banking system amounted to 161, insurance companies totaled 44 and intermediary agencies specializing in insurance reached 227.
Substantial progress has been achieved in the opening up of the financial sector in Beijing. Since RMB business was opened to foreign funded banks on 1st of December, 2004, 10 foreign funded banks have officially launched RMB services. By 2005, altogether 25 branches, four sub-branches, 78 agencies of foreign funded banks and 17 solely-foreign funded and joint stock insurance companies have been established in Beijing.
Main Financial and Insurance Organizations in Beijing



(v) Foreign Exchange
Beijing has increasingly s t r e n g t h e n e d e x c h a n g e s with other countries and regions all over the world in economy, trade, science and technology, education, culture and other fields. Governments, communities and social organizations conduct active cooperation. Currently, Beijing maintains partnerships with 38 cities of 34 countries around the world. There are 137 foreign embassies, 17 international organizations and local agencies and 190 foreign news agencies in Beijing. Foreign agencies in Beijing number over 7,000 and there are over 17,000 foreign students.
The major cities maintaining partnerships with Beijing are as follows:

Exhibition
Beijing's exhibition industry is of great importance for the whole country. The major exhibition centers include: Beijing International Convention Center, China International Science and Technology Convention Center, China International Exhibition Center, China National Agricultural Exhibition Center, Beijing Exhibition center, China International Trade Exhibition Center. In 2005, the area of hotel rooms and boardrooms of these venues in Beijing reached 621,000 m2 and the exhibition halls, 204,000 m2. Nearly 7,000 international conferences were held with a total revenue of 320 million yuan. In addition, 322 international exhibitions were held in Beijing in 2005.
(Vi) Scientific Research and Education
Scientifi c Research
Beijing is the largest base for scientific and technological research in China, with the Chinese Academy of Science and other scientific research institution and Zhongguancun Scientific Park, which is known as China's Silicon Valley, of which achievements awarded by the central authorities account for one-third of the total every year. By 2005, there were 7,400 organizations and institutions involved in scientific activities with 340,000 professionals, with a total of 38 billion yuan allocated for research and experiments in Beijing.
Education
Beijing is home to a large number of higher education institutions and welleducated people. There is a total of 79 higher education institutions in Beijing, including Peking University, Tsinghua University, Renmin University of China and Beijing Normal University. In the year 2005, there were 117,000 graduates, 156,000 new students, 537,000 in-school students, 113,000 faculties and other personnel and a floor space of 25.985 million m2. Higher education institutions qualified to recruit graduate students totaled 51 with 31,000 graduates, 52,000 new students and 142 thousand in-school students. There are 24 libraries in Beijing, including the largest one in Asia and there are also over a hundred museums in Beijing.
(vii)Tourism and Special
Local Products
Beijing boasts abundant tourism resources with more than 200 tourism sites open to the public, including Tiananmen Square, Beijing Ancient Observatory, the Workers' Cultural Palace, the Imperial Palaces of the Ming and Qing Dynasties (the Forbidden City), the Lama Temple, Zhongshan Park, Shichahai, Beihai Park, Miaoying Temple, Prince Gong Mansion, Jingshan Park, Taoranting Park, the Temple of Heaven, the Fragrant Hills, the Summer Palace, the Ruins of the Old Summer Palace, Zizhuyuan Park, the Temple of the Sun, Lugou Bridge (Marco Polo Bridge), Mount Ling, Mount Miaofeng, Tanzhe Temple, the Imperial Tombs of the Ming Dynasty, Badachu Park, Badaling Great Wall, Shidu and the Peking Man Site at Zhoukoudian.

II . Economy
(i) GDP
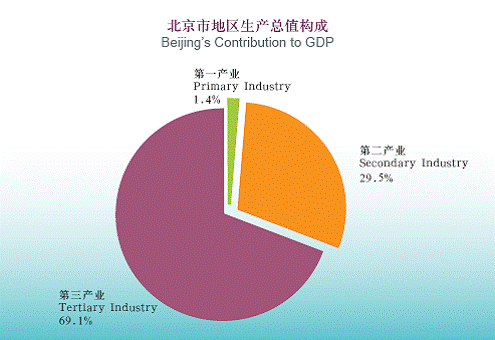
In 2005, Beijing's GDP totaled 688.63 billion yuan and per capita GDP reached 45,444 yuan. The added value of primary industry came to 9.8 billion, secondary industry of 202.65 billion yuan and tertiary industry of 476.18 billion yuan.
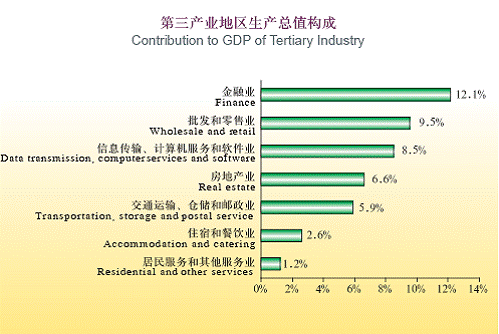
(ii) Resources, Agriculture and Industry
Natural Resources
Beijing boasts a favorable condition for mineral resources. Other capitals around the world seldom enjoy this kind of advantage. It also stands out from other major cities in China for its large amount of proven reserves of a variety of ores. Currently, 126 kinds of minerals have been found in Beijing. The reserves of 68 kinds are verified and 363 mines have been set up. Among the mines of verified reserves, the large-scale mines total 30, accounting for 8.6%, medium-scale total 106, accounting for 30.6%, small-scale total 96, accounting for 27.6% and miniscale total 115, accounting for 33.2%. The major minerals include coal, iron ore, gold, molybdenum, limestone for cement, marble, diopside and sand for construction etc.
Ground water is among the most important resources in Beijing. The ground water replenishment is 3.95 billion m3/a and the yield totals 2.63 billion m3/a. The yield in the plain reaches 2.46 billion m3/a. Ground water accounts for two-thirds of the city's water supply, with more than 150 water sources for Beijing's urban areas, rural areas, satellite towns, large-scale mines and various organizations and institutions. After the middle section of the South-North Water Transfer Project is launched in Beijing, ground water will account for half of the city's water supply.
Beijing enjoys abundant terrestrial heat resources. Preliminary data demonstrate that areas with terrestrial heat cover 2,372 km2, constituting 14.1% of the total area of Beijing. The quantity of heat in the reserve layer is equal to that produced by 11 billion tons of standard coal. The total reserve of terrestrial heat reached 18.12 billion m3, out of which 110 million m3 are to be explored every year, equal to the quantity of heat produced by 649,000 tons of standard coal.
Agriculture
In 2005, the output value of the service industry in farming, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery in Beijing totaled 26.88 billion yuan, with farming contributing 10.06 billion yuan, forestry of 1.33 billion yuan, animal husbandry of 13.57 billion yuan, fishery of 970 million yuan and services for the above four sectors of 950 million yuan.
Industry
In 2005, the major industrial enterprises in Beijing realized an added value of 170.54 billion yuan and export products of 106.53 billion yuan. High-tech industries achieved an added value of 51.75 billion yuan, accounting for 30.3% of the total in Beijing.
Output of Major Industrial Products of Beijing

(iii)Commercial Data
Foreign Trade
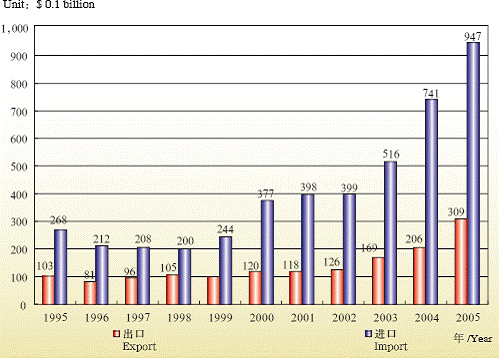
In 2005, Beijing's cargo trade volume reached $125.57 billion, with an export volume of $30.87 billion and import volume of $94.7 billion. The export volume of mechanical and electrical products totaled $15.63 billion, accounting for 50.5% of the region. That of high-tech products came to $9.74 billion, accounting for 31.5% of the region. According to Balance of Payments, service trade volume reached $29.16 billion, with revenue of $18.2 billion and expenditure of $10.96 billion.
Beijing's Cargo Trade
Service Trade Revenue and Expenditure

Utilization of Foreign Funds
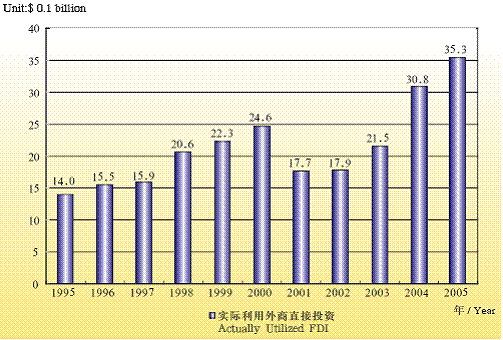
By 2005, 126 countries and regions had investments in Beijing. Among them, Hong Kong established 8,176 foreign funded enterprises with FDI reaching $15.29 billion, accounting for 30.6% of the total contracted foreign fund; British Virgin Islands, 1,296 enterprises with FDI amounting to $5.87 billion, constituting 11.8% of the total; Japan, 2,032 enterprises with FDI $5.57 billion, accounting for 11.2%; United States, 4,004 enterprises with FDI $4.79 billion accounting for 9.6%; Germany, 378 enterprises with FDI $2.44 billion accounting for 4.9%; Korea, 1,729 enterprises with FDI $2.44 billion accounting for 4.5%; Cayman Islands, 351 enterprises with FDI $2.03 billion accounting for 4.1%.
Actually Utilized FDI in Beijing
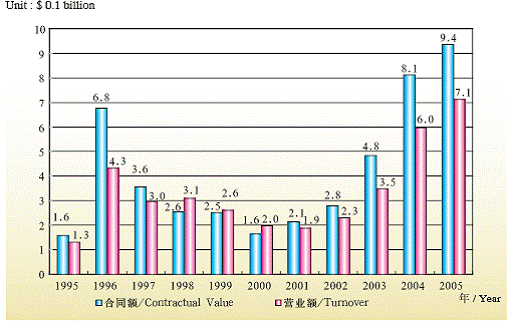
Foreign Economic Cooperation
In 2005, Beijing's contracted projects and labor service cooperation with foreign countries realized a turnover of $712.81 million with contracted capital of newly signed contracts amounting to $937.32 million. 3,473 laborers were sent abroad and people working in foreign countries numbered 4,796. Major projects exceeding $10 million amounted to 17 with total contracted capital reaching $380 million.
Contracted Projects and Labor Service Cooperation in Beijing
In 2005, five enterprises in Beijing were responsible for 49 foreign aid projects including six engineering foreign aid projects with a total contractual value of $6.96 million, 16 goods foreign aid projects, 14 design, consultancy and engineering supervision projects and 13 other projects. Countries receiving aid include Mauritius, Tonga, Togo, Guinea-Bissau, Antigua, Mauritania and Afghanistan etc.
In 2005, the Beijing municipal government approved 51 foreign enterprises and institutions including 19 foreign institutions and 32 foreign enterprises. Total value of investment in foreign countries amounted to $204.4375 million with contracted investment value on China's part reaching $204.0514 million, accounting for 99.81% of the total. There are eight American projects with investment in trade, tourism, electronics, computer software, Internet and other fields.
Commodity Circulation
In 2005, the total value of goods purchase amounted to $1.23087 trillion. Of this, 412.11 billion worth of goods was purchased in Beijing and 645 billion worth of goods, outside the city. Sales of commodities reached 1.34 trillion yuan with 595.86 billion yuan worth of goods sold in Beijing, 675.45 billion yuan outside the city and 68.7 billion yuan abroad.
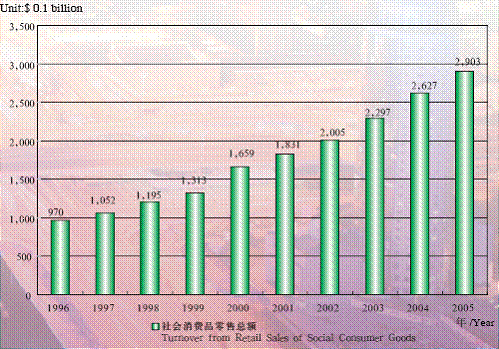
In 2005, turnover from retail sales of consumer goods reached 290.28 billion yuan in Beijing, with turnover in the urban area amounting to 251.91 billion yuan and in rural areas, 38.37 billion yuan. The turnover from wholesale and retail trade totaled 252.94 billion yuan,with 26.79 billion yuan from catering retail, and 10.55 billion yuan from other sectors.
Turnover From Retail Sales of Social Consumer Goods in Beijing
In 2005, the CPI (Consumer Price Index) of Beijing residents was 101.5%, including CPI for food, 104.9%, CPI for tobacco, alcohol and daily necessities, 100%, CPI for clothing, 100.1%, CPI for household equipment and repair services, 99.7%, CPI for medical care and personal articles, 98%, CPI for transportation and communication, 97.5%, CPI for recreational and educational articles and services, 99.7%, CPI for accommodation, 105.9% and CPI for retail commodities, 99.7%.
III . Investment
(i)Policy and Administrative Rules
Catalogue of Related Laws
Foreign Trade Law of the People's Republic of China
Customs Law of the People's Republic of China
Law of the People's Republic of China on Import and Export Commodity Inspection
Law of the People's Republic of China on Chinese-Foreign Equity Joint Ventures
Law of the People's Republic of China on Chinese-Foreign Contractual Joint Ventures
Law of the People's Republic of China on Foreign-Capital Enterprises
Company Law of the People's Republic of China??
Law of the People's Republic of China on the Entry and Exit Animal and Plant Quarantine
Law of the People's Republic of China on Control of the Entry and Exit of Aliens
Law of the People's Republic of China on the Control of the Exit and Entry of Citizens
Securities Law of the People's Republic of China
Income Tax Law of the People's Republic of China for Enterprises with Foreign Investment
and Foreign Enterprises
Individual Income Tax Law of the People's Republic of China
Law of the People's Republic of China on the Administration of Tax Collection
Environmental Protection Law of the People's Republic of China
Law of the People's Republic of China on Evaluation of Environmental Effects
Law of the People's Republic of China on Promotion of Cleaner Production
Law of the People's Republic of China on Prevention and Control of Desertification
Marine Environment Protection Law of the People's Republic of China
Law of the People's Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Atmospheric Pollution
Law of the People's Republic of China on Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution by Solid Waste
Law of the People's Republic of China on Prevention and Control of Water Pollution
Law of the People's Republic of China on Prevention and Control of Environmental Noise Pollution
Law of the People's Republic of China on Prevention and Control of Radioactive Pollution
Frontier Health and Quarantine Law of the People's Republic of China
Labour Law of the People's Republic of China
Trade Union Law of the People's Republic of China
Searching Website for the Related Laws
1 . Searching System of Laws and Regulations of China (website of National People's Congress of China)
http://law.npc.gov.cn:87/home/begin1. cbs
2. China Legislative Information Network System
http://www.chinalaw.gov.cn/jsp/jalor/index.jsp
3. Ministry of Commerce
http://www.mofcom.gov.cn
the above-mentioned websites are for reference only.
(ii) Guidance for Foreign Investment
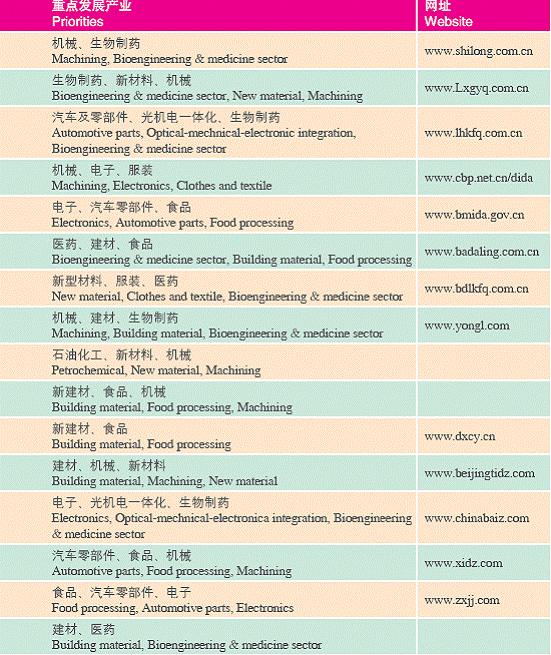
1. Industries
The focuses are on: (1) Electronics and information industry; (2) Automobile industry; (3) New petrochemical materials; (4) Bioengineering and new pharmaceuticals; (5)Advanced equipment manufacturing; (6)Metropolitan industries
2. Agriculture
Highlight the imports of high-tech and new-agricultural technologies and the construction of modern farming bases; imports of advanced-crop and animal strains, techniques, equipment and experts to eventually enhance the agricultural sectors ability to produce via intensive, industrialized operations.
3. Commerce
Development of supermarkets, convenience shops, specialized product shops and shopping centres. Promote the development of modern logistics, chain businesses, e-commerce and networking businesses.
4. Tourism
Focus on the intensive promotion of the development of tourism-related facilities, including infrastructural facilities, tourist and recreational facilities, tourist information services, the development of transportation and communications as well as the development and operation of tourist sites. Set up joint-venture tourist agencies and enhance cooperation with foreign tour operators to expand the business scope of the local tourist agencies.
5. Financial and insurance industries
6. Cultural and social undertakings
(iii) Procedures for Enterprise Establishment
How to invest
For foreign investors, any of the following business modes may be used to establish a business entity in Beijing: a joint venture, cooperation, solely foreign-owned enterprises; a foreign-funded joint-stock limited company, cooperative development, foreign companies seeking investment, and group company for foreign investment enterprises. To attract and encourage foreign investment, Beijing is striving to improve its investment environment and to explore and expand BOTs (build-operate-transfer) and will engage in multinational mergers and new forms of investment.
Limit of Authority for Examination and Approval
(1) According to the categories listed in the Industries List for Foreign Investment (2004 edition), encouraged projects and allowable projects with total investments of US$30 million$100 million (including added-capital, as with the projects listed immediately below) as well as restrictive projects with a total investment less than US$500 million shall be approved by the Development and Planning Committee of the Peoples Government of Beijing Municipality (MDPC). Encouraged projects and allowable projects with a total investment above US$100 million as well as restrictive projects with total investments above US$500 million are audited by the Beijing Commission for Development and Reform of the Peoples Government of Beijing Municipality and submitted to the National Development and Reform Commission of the Peoples Republic of China for final approval. Encouraged projects and allowable projects with investments valued at less than US$30 million are approved by the Beijing Economic and Technological Development Area (BDA), the Beijing Tianzhu Export-oriented Processing Zone and the Development and Reform Department of each district and county.
(2) The establishment and alteration of foreign-funded enterprises and relevant articles of contracts and the related revisions (inclusive of foreign-investment merging) shall be approved by relevant municipal, district, or county bureaus of commerce or the Beijing Economic and Technological Development Area (BDA), the Tianzhu Export-Oriented Processing Zone or the Zhongguancun Science Park Haidian Administrative Commission. The authority of each of the said institutions allows them to encourage and allow enterprises with total investments (including added
capital and mergers, as with projects listed below) of less than US$30 million, which shall be approved by responsible departments of commerce and foreign investment authorities in each relevant district , development zone, export-oriented processing zone or science and technology park. Encouraged and allowable enterprises with an investment of US$30 million (inclusive)US$100 million, as well as restricted enterprises with total investments of less than US$50 million, shall be approved by the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Commerce. Encouraged and allowable enterprises with total investments exceeding US$100 million as well as restricted enterprises with total investments above US$500 million shall be audited by the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Commerce and then submitted to the Ministry of Commerce of the PRC for final approval.
If additional application procedures and approaches for foreign investment projects have been stated in State statutes or administrative regulations, the said procedure and approach must be followed. The foreign investment projects that need the Stotes and the city's overall consideration and these in accord with the gradual opening up trend must comply with State regulations.
Procedural Chart for Establishment of Joint Ventures, Co-operative and Completely Foreign-funded Enterprises
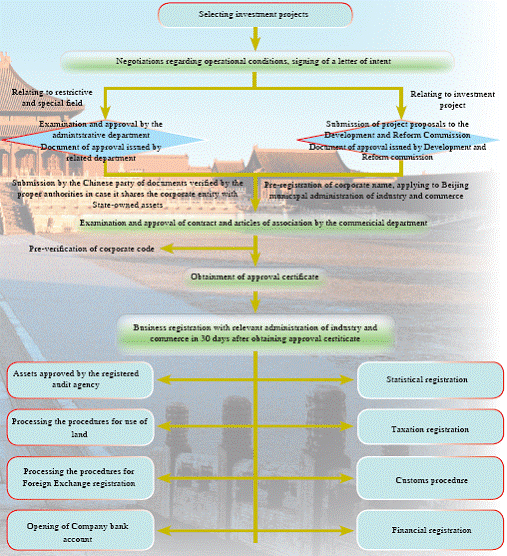
(iv) Reference Prices of Basic Elements
1 Benchmark Land Price
Unit: yuan per square metre
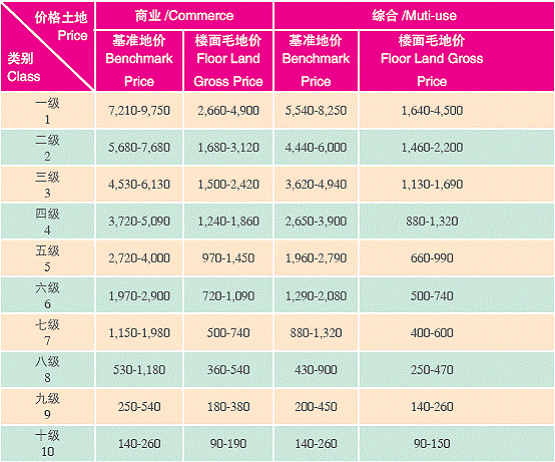
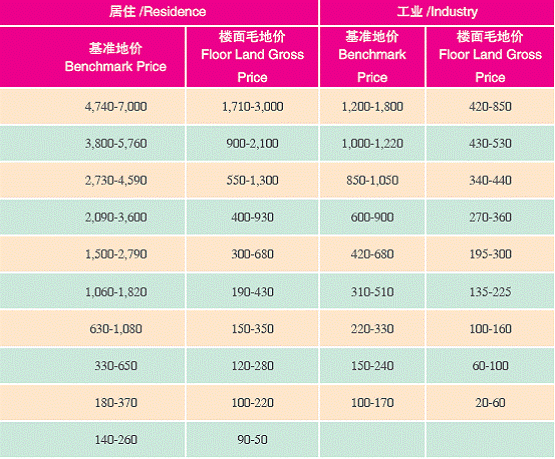
Note 1: The surface area gross price contains two sections. One refers to the amount of money the government collects for selling the land with its longest use period; the other refers to the average price per square metre of land for municipal infrastructural compatible construction.
Please refer to Beijing Municipal Administration of State Land, Resource and Housing Web site www.bjgtj.gov.cn
Consult the No. 32 (2002) notice from the General Offi ce of the People's Government of Beijing Municipality about the adjustment of standard prices for State land. For further information, Please refer to http://www.bjgtj.gov.cn
2. Land Prices for Foreign-invested Enterprises
Unit: yuan/square metre/year
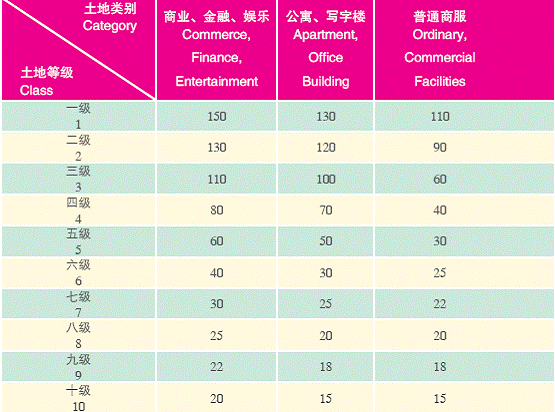
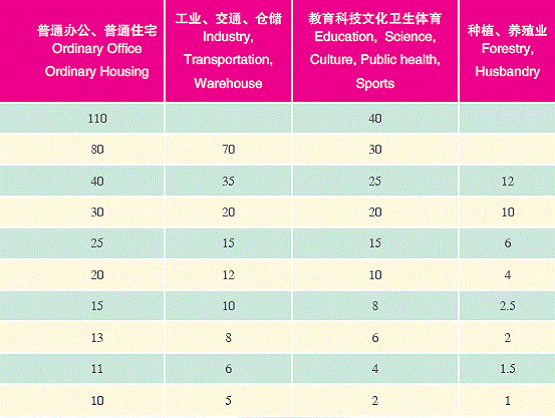
Please refer to http://www.mlr.gov.cn for more information about Beijing's land categories for foreign-invested companies and Beijing's standards for various land grades.
3. Current Water Price
Unit: yuan/ton
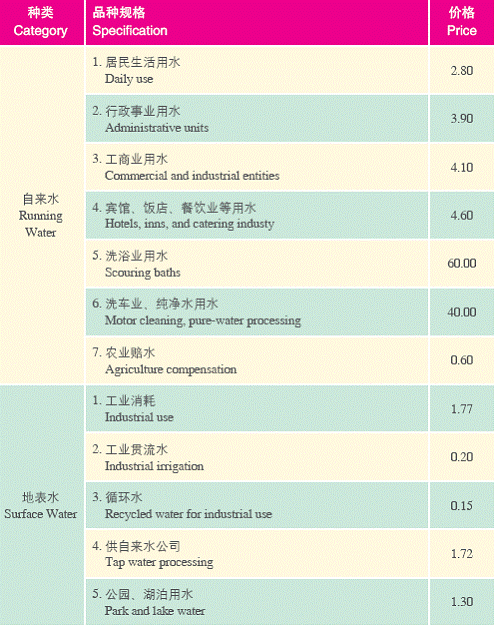

4. Electricity Price
Unit: yuan/kilowatt hour


5. Heating Supply Price
Unit: yuan/construction square metre during the?? heating?? season
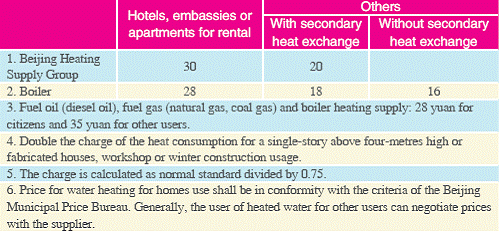
6. Gas Prices
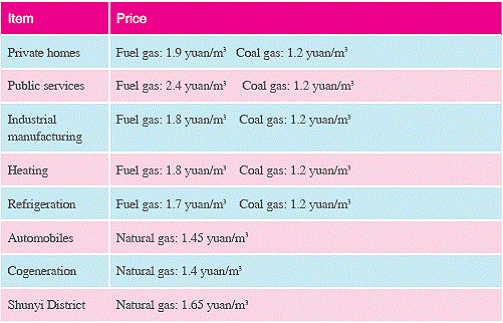
Note: For more details, please consult the No. 141 (2003) Notice about the Adjustment
of Gas Prices by the Beijing Municipal Price Bureau
See: http://www.china5e.com/dissertation/naturalgas/0216.htm
7. Communication Prices

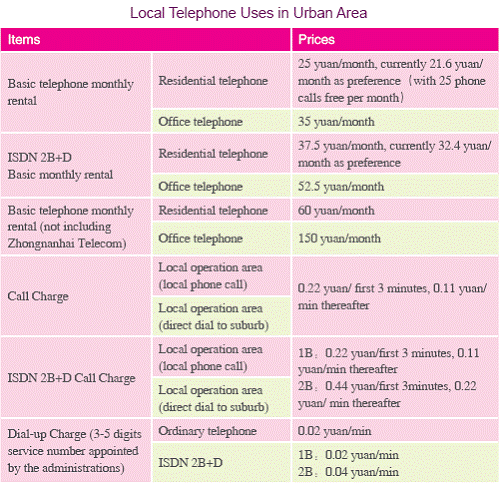
IV . Development Zones
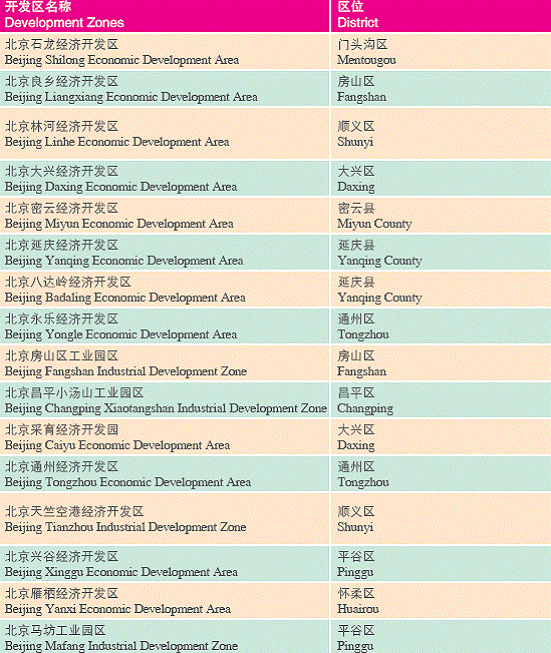
(i) State-level and Provincelevel Development Zones
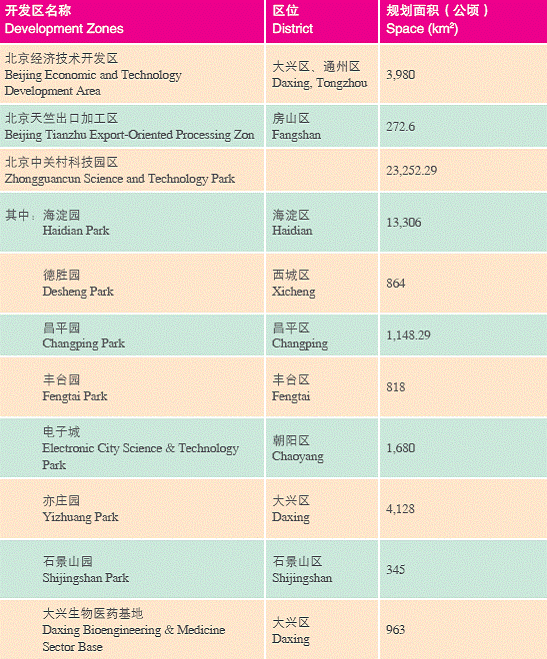
Beijing Economic and Technology Development Area
The Beijing Economic and Technological Development Area, also known as the Beijing Development Area (BDA), is the only State-level development zone in the Chinese capital, which enjoys policy privileges granted by the State to both Statelevel development zones and State-level high-tech industrial zones. According to the general plan of BDA, it covers 46.8 square kilometres, which includes an industry area, a business area and a residential area.
In line with the industrial policies of the State and the principle of the local government that calls for concentrating on building up a high-tech based industrial establishment of Beijing, the BDA favours foreign-funded, high-tech and export-oriented enterprises. The BDA also favours electronic information, pharmaceuticals, automobile industries and others.
About 1,800 companies were operating in the area at the end of 2005, which involved a combined investment of US$10.913 billion; and the production value of Hi-tech enterprises took up over 87% of the total industrial value. And more than 80 well-known multinational enterprises have settled at BDA, namely Nokia, GE, Corning, SMC, Cummins, Schneider Electric, Panasonic, SMIC, Foxconn, Bayer,
Daiichi and Novo Nordisk etc.
Beijing Tianzhu Export-Oriented Processing Zone
Beijing Export-Oriented Processing Area, is Beijing's only State-class exportoriented
processing area with a developed area of 1.25km2. As a customs' special area under closed management, the area operates according to international practices to provide export-oriented processing enterprises with an easier and more convenient operational environment. The total investment of production base reached 400 million USD, mainly from USA, UK, Japan and Hong Kong SAR. The newly established Modern Automobile City, New International Exhibition Center and Venues for 2008 Olympic Games have made here an energetic area of industry, commerce, exhibition and service trade.
It is located one kilometre from the Beijing Capital International Airport.
Zhongguancun Science and Technology Park
The ZSTP was inaugurated in May 1998 with approval of the State Council, as the country's first state-level, new- and high-tech development zone. Geographically, in includes Beijing's scientific research, knowledge, human and information resources. There are 39 colleges,such as Tsinghua University, Peking University,with 400,000 students in the development zone, as well as 213 various scientific institutions represented by China Academy of Sciences. By 2005, the zone had 17 thousand high-tech enterprises in total, with sales income of over 480 billion yuan, about one seventh of all high-tech enterprises in China, with added value of 96 billion yuan, about 14.1% of GDP in Beijing.

(ii) Service Offi ces
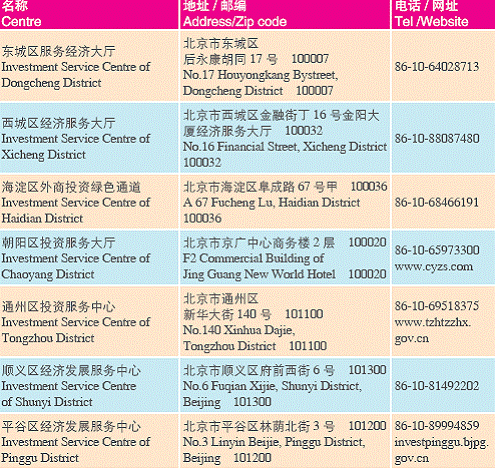
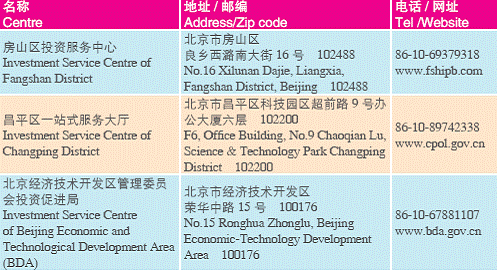
1. One-stop Investment Service Centres in Beijing

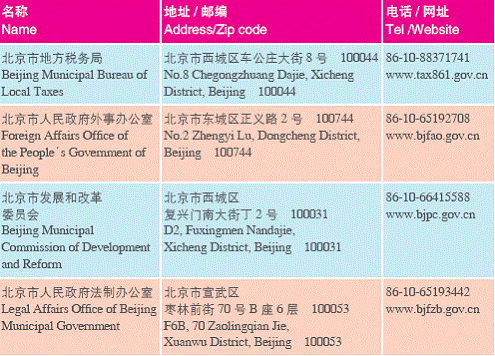
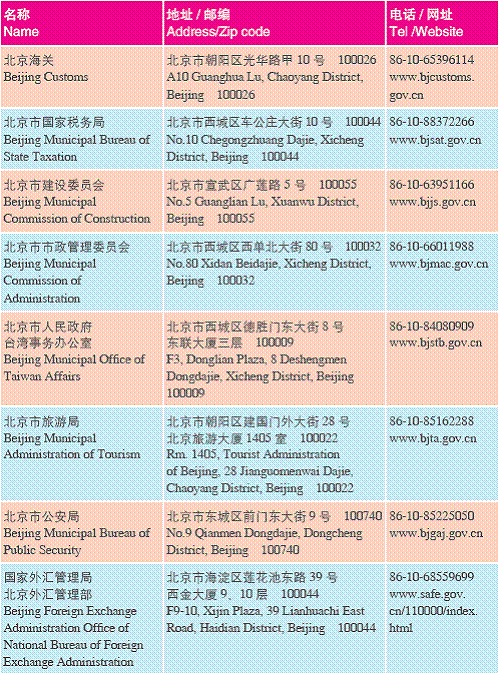
2. Government Offi ces


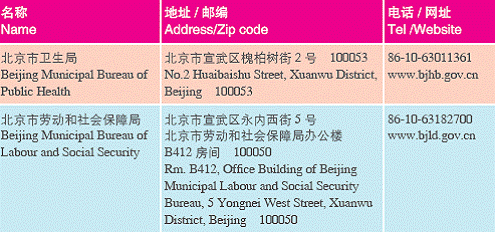

3. Others Service Organizations
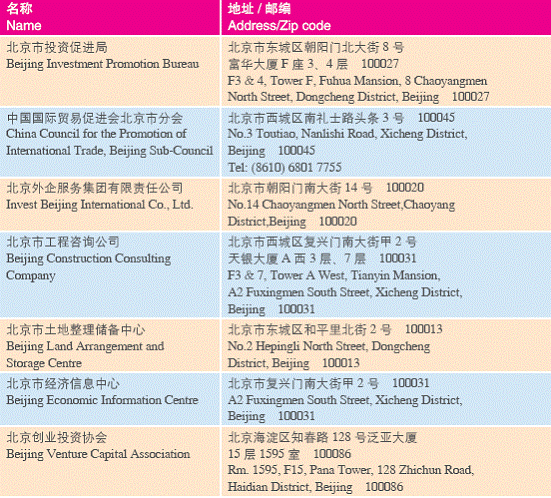

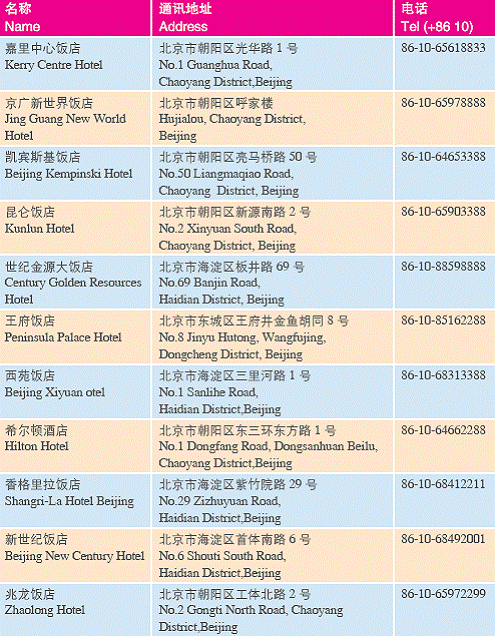
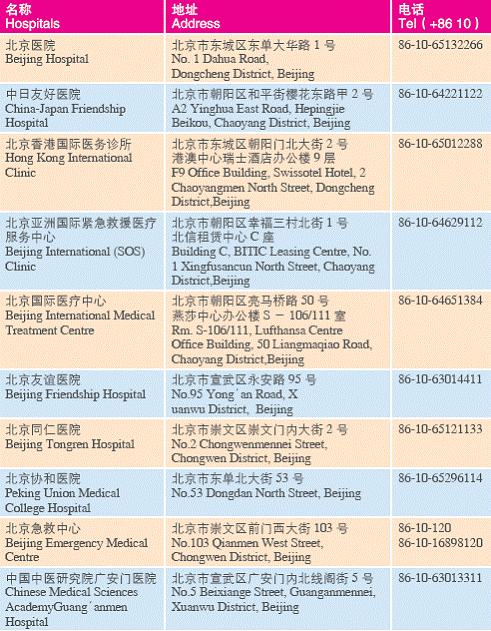
Appendix
1. Hotels

2. Recommended Hospital
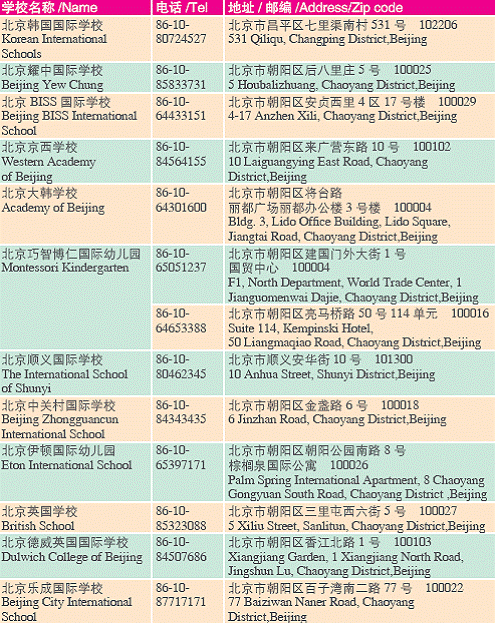
3. Schools
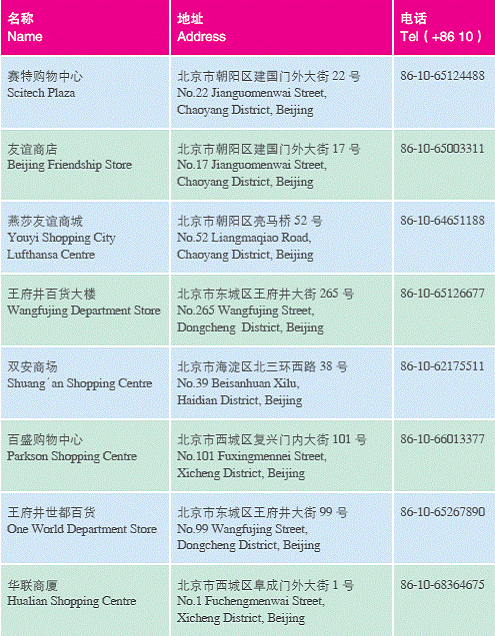
4. Shopping Centres
5. Beijing Airport and Airline Companies
Beijing Capital International
Airport: +86 10 6752 2114??www.bcia.com.cn
Hotline: 962580

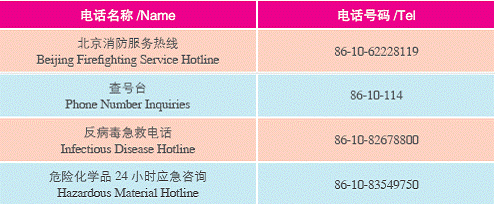
6. Handy Phone Numbers
(Ministry of Commerce June 24, 2009)