I . Survey
(i) Geographical Location
Shanghai is situated at 31’14’ north latitude and 121’29’ east longitude. It is in the east of Yangtze River Delta, also assumes the central location along China’s coastal line. The city has a total area of 6,340.5 square kilometers. In the 16th century, Shanghai became the national center of textile & handicraft industry. By the mid-19th century, Shanghai has become a major trading port, China’s largest industrial city and the Financial Center in the Far East. With its ever increasing dynamism, Shanghai has become one of the most important economic hubs of the country.
(ii) Climate
With a pleasant northern subtropical maritime monsoon climate, Shanghai enjoys four distinct seasons, generous sunshine and abundant rainfall every year. The weather is generally warm and moist, and its spring and autumn are relatively short comparing with the summer and winter. In 2005, the average annual temperature was 17.5 degrees Celsius. The city had a total sunshine time of 1,778.3 hours in 2005 and received a total rainfall of 1,254.9 millimeters. However, about 70% of the precipitation came during the May-September flood season.
(iii) Population and Nationalities
By the end of 2005 , Shanghai’s residential population had reached 17.78 million, among them, 11.4894 million are non-farmers, while 2.1132million live on farms. The majority is of the Han nationality.
(iv) Urban Infrastructure and
Transportation
Milestone progress has been made in the building of“ Three Ports and Two Networks”, referring to the Deep Water Port, Aviation Port, and Information Port, railway and highway networks respectively, and the city’s spill-over economic effect has been therefore enhanced.
Airport
Shanghai has two airports off the city, namely, Hongqiao Airport and Pudong Airport. In the year of 2005, 375,100 flights took off and landed in the two airports, carrying 41.3916 million passengers into and off the city. Among them, 26.7987 million were by domestic lines, and 14.5929 million by international and regional lines. In 2005, Shanghai maintained flight connections with 181 cities and regions including 98 overseas cities and districts. Shanghai provides lines with all the rest of China, including Hong Kong and Macao. There are 65 airline companies operating in Shanghai, of which 52 are foreign airlines. In 2005, the total amount of airborne cargo through the Shanghai airports reached 2.21 million tons, ranking Shanghai among the Top 10 airports in the world.
Sea-Port
Shanghai is China’s top sea port. Up to the end of 2005, there are 28 container docks, and 124 deep-water berths of 10,000 tonnages each. Shanghai Port has established business connections with over 500 ports of 200 countries/regions. It operated 16 international container shipping routes with business contacts to 12 navigating zones around the world. In 2005, Shanghai Port handled 443 million tons of cargo, making it the largest port in the world. In the same year, the city’s port handled 18.084 million TEUs, ranked the third largest worldwide.
Shanghai started the construction of Yangshan Deepwater Port in 2002. On December 10, 2005, the first phase of Yangshan Deepwater Port was completed. Five 70-100 thousand tonnage berths of the first phase have been built and come into operation, with a capacity to deal with over three million TEUs each year and it offers all-weather service to any types of largest containerships. Yangshan Deep Water Port, also houses the Yangshan Bonded Zone, which is the first of its kind in China, integrating all the functions as a port, a bonded zone, an export processing zone and a bonded logistics zone.
Roads
Up to the end of 2005, Shanghai has 560 km expressways, carrying 327 million tons of cargo and 24.68 million passengers. The network of roads has linked Shanghai with 392 counties under 104 prefectures in the other provinces and municipalities.
In 2005, the metro system in Shanghai has extended to 123 km. By the end of 2005, there are 940 bus routes with a total route length of 21,794.45 km. The total road surface reached 75.8 million square meters, and the total length 8,110 km. The density of road network is 128 km. per 100 sq. km.
Railways
In 2005, the trains dispatched by Shanghai railway authorities covered 269.1 kilometers, transporting 12.783 million tons of cargo, and 43.131 million passengers. Shanghai Railway Station has a daily capacity of transporting 110,000 departing passengers on average.
Finance and Insurance
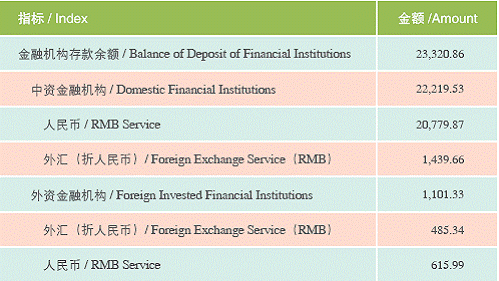
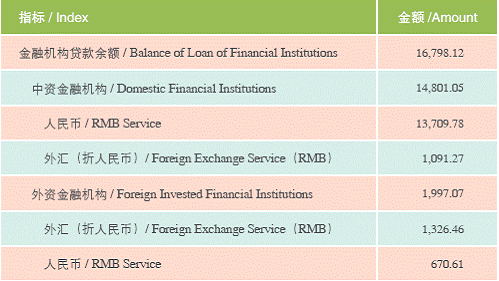
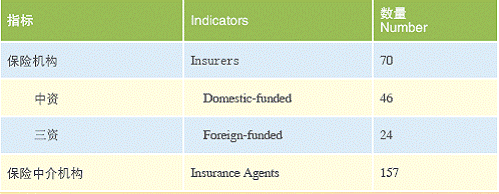
Shanghai has basically formed the financial market system with the markets of currency, capital, foreign exchange, futures, gold and equity as the main part. The total assets of all the financial institutions have reached 3.2 trillion RMB, accounting for 9% of that of the nation. In 2005, the total volume of the financial market exchange was 35 trillion RMB. By the end of 2005, Shanghai had been home to 610 financial institutions, which was 3.3 times as many as in 2001. Among them, 231 were banking institutions, 110 security ones, and 269 of insurance nature. Over 30 financial institutions, which play an important role in promoting the cohesive and radiational functions of Shanghai as an international financial center, such as the Gold Exchange, China Union Pay and the business operation head-offices of national financial institutions, such as credit card centers, bills centers, fund operation centers, data centers, etc., and over 10 new-type institutions such as currency brokerage companies, agricultural insurance companies, auto-financing companies, assets management companies, etc.
In 2005, Shanghai called home to 320 foreign-invested financial institutions. The capital assets of all the foreign-invested banks have accounted for 50% of the banking industry in China. The capital assets plus the loan volume in the city have accounted for 10% share of the local market. 28 foreign-invested banks have chosen Shanghai as the location for major reporting bank in China, accounting for 70% of the total number of the China-based foreign-invested major reporting banks. The premium generated by foreign insurance companies has taken up to 17% of the market.
Balance of Deposit and loan of Financial Institutions (2005) Unit:100 million RMB
Insurance Agencies and Related Intermediaries (2005) unit:1
Telecommunications
By the end of 2005, Shanghai had 9.967 million fixed line telephone users(penetration rate:56.1%), 1.884 million Smart Phone users, 6.85 million household phone users (penetration rate over 100%), 14.442 million mobile phone subscribers (penetration rate:81.2%),and cable TV subscribers of 4.273 million (penetration rate:67%).
Internet
Shanghai’s Internet international connection bandwidth has been expanded to 30G. There have been 8.03 million Internet users and 2.474 million subscribers to broadband access in the city, among which 2.2266 million are household users. Currently, more than 1,300TB of data streamed through the city’s WWW Exchange Center, with the highest daily data flow hitting 5 TB. The total exchange of data flow through routers could reach 26 Class B IP addresses, with the bandwidth up to 4.9G.
(v) International Relations
Sister cities
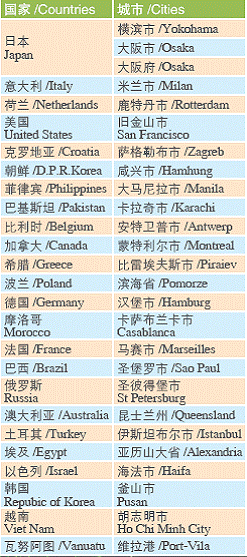
By the end of the year, the city had established sister-City ties and long-term friendly exchange programs with 66 cities (provinces, states and regions) in 50 countries around the world.
Cities with Sister-city Relationship
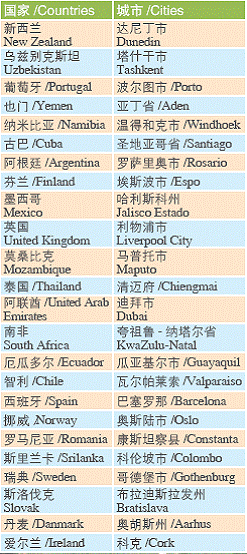
Cities with Friendly Exchange Relations
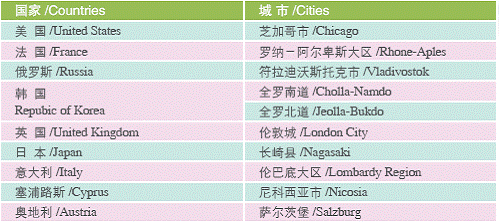
International Exhibitions
By the end of 2005, the floor area of the city’s exhibition halls reached 3.76 million square meters. In the year of 2005, Shanghai hosted 276 exhibitions, including the 17th IBLAC Meeting, the 7th Shanghai International Industrial Fair, the 15th East China Fair, the 4th Shanghai International Sourcing Fair, 2005 World Bus Fair (Asia). Exhibition giants, such as Deutche Messe AG, Fiera Milano of Italy and Messe Frankfurt GmbH, have set up their branches in the city.
Since 1989, Shanghai has organized 18 sessions of IBLAC Meeting. On November 5, 2006, the 18th IBLAC Meeting has attracted over 30 Chairmans and CEOs of MNCs to speak on the meeting, contributing their advices for Shanghai’s further development, demonstrating their firm confidence in Shanghai’s future.
Shanghai International Industry Fair
Since 2006, Shanghai International Industry Fair has been upgraded to China International Industry Fair, the only large size industry exhibition showcasing the latest high tech products and technologies and providing trading floor to the technology and product exchanges. SIF2006 is a reflection of the country’s development plan, showcasing the machine tools, industry automation, environmental protection, energy and IT technology and machinery home and abroad. Its grand scale and high degree of professionalism make it one of the most important international events for the equipment manufacturing industry of China.
East China Fair (ECF)
East China Fair (ECF) is co-sponsored by 9 provinces and cities, namely Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, Jiangxi, Shandong Province and two cities Nanjing and Ningbo. Since 1991, East China Fairs have been held 16 times successfully. The 16th ECF designated four exhibition areas of garment, home textiles, decorations, daily consumables, where the exhibiting enterprises were from 26 provinces and cities. The ECF has become the largest regional international economic fair in terms of its scale, number of exhibitors, scope of infl uence and its trade volume.
China International Sourcing Fair (Shanghai)
In 2006, the first China International Sourcing Fair (Shanghai) has been coorganized by Ministry of Commerce & Shanghai Municipal People’s Government, supported by the foreign trade & economic cooperation authorities from more than 18 provinces and cities in China, including Tianjin, Chongqing, Shan’xi, Hubei, Yunnan, Shandong, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Liaoning, Fujian, Sichuan, Guangdong, Hebei, Hainan, Jiangxi, Beijing, Anhui and Xinjiang. This CISF, originally named Shanghai International Sourcing Conference for the past four years, has become one of the most influential reverse sourcing fair in China.
World Expo 2010
On December 3rd, 2003, China has won the bidding to host 2010 World Expo. The theme of Shanghai World Expo is “Better City, Better Life”. From May 1st to October 31st, 2010, the bund area stretching from Nanpu Bridge to Lupu Bridge will be the location for the Expo2010, which will attract 200 countries and international organizations, as well as 70 million people across the world. It is expected that Expo 2010 Shanghai, China will be the successful, wonderful and unforgettable world expo of its kind, expecting the widest possible participation in the history of the World Expositions. Shanghai World Expo will provide extensive business opportunities, including the planning and construction of the Expo zones, the designation of partners and key sponsors, the organization of exhibitions and conferences, tourism, consultation and management services, wholesales and retails, HR services, media industries. 2010 World Expo will be an event for the exchanges of human beings’ urban experiences, a symposium on “innovation” and “integration”, a time for cross-culture dialogue.
(vi) High Education and Science and Research Development
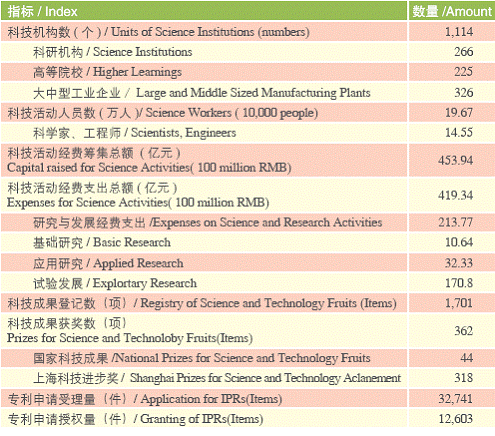
As of late 2005, Shanghai had 60 regular institutions of higher learning, including Fudan University, Jiaotong University, Tongji University etc. They enrolled 131,800 undergraduate students for 3-or-4–year programs, making a total population of 442,600 students. The number of newly recruited postgraduates hit 27,700, while 16,700 graduated, 3,230 of them with a doctoral degree and 13,511 with a master’s.
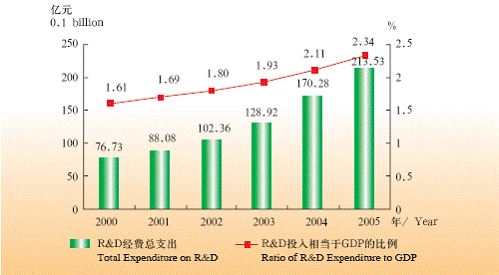
By the end of 2005, the city had 97 academicians with the Chinese Academy of Sciences and 67 academicians of the Chinese Academy of Engineering. In 2005, the city allocated 21.4 billion RMB on R&D expenses, accounting for 2.34% of the city’s GDP.
Index on Science and Research in Shanghai (2005)
Expenditure on R & D of Shanghai
(vii) Tourism
Shanghai is a cultural city with long and glorious history. Up to now, Shanghai has retained many historical sites and the rich characteristic botanic gardens from Tang, Song, Yuan, Ming, Qing Dynasties. Shanghai has more than 1,000-year-plus Long Hua Temple, Jing’an Temple constructed in Three Kingdom Times, Yufo(Jade Buddhist) Temple well-known home and abroad, Yu Garden famous for its South China garden style, Confucius Temple in Jiading District, Square Tower and Zui Bai Chi Pond in Songjiang District. Since 1990s, Shanghai completed a group of functional constructions that enjoy a good reputation, which as part of the enchanting city landscape, showing people a new outlook of Shanghai, including the Bund, People’s Square, Oriental Pearl TV Tower, Jin Mao Tower, Nanjing Road Pedestrian Street, Shanghai Museum, Shanghai Grand Theater, Shanghai Urban Planning Exhibition Center, etc. Shanghai provides a complete range of tourism facilities, including 25 five-star hotels, and 52 international tourist agencies. In 2005, Shanghai has received 5.714 million foreign tourists.
Yu Garden
Construction of Yu Garden started in 1559. Its layout features the garden styles of south-of-the-Yangtze region in China during the Ming and Qing Dynasties. Enjoying a lasting reputation as“ Wooded Hill in City,” the garden is very well preserved. Carved dragons wind across atop the walls, which divide the garden into different scenes. The pavilions, ponds, man-made stone formations have formed 48 scenic spots in this small garden.
New Bund
The New Bund lies along the west bank of the Huangpu River between the Waibaidu Bridge, also known as Garden Bridge, and Nanpu Bridge. The four-kilometer-long thoroughfare was listed as one of the top 10 new scenes and tourist attractions in the city. Along the Bund, there are buildings of different Chinese and western architectural styles, nicknamed the“ contemporary expo of world architectures”. This cultural heritage of mankind has epitomized the modern history of Shanghai. At night, with lights on, they look just fantastic.
People’s Square
Located at the very center of the city, People’s Square is a garden-type open space surrounded by buildings and administrative facilities, as well as cultural activities, transportation and commerce. To its north is the People’s Mansion, to its northwest the Shanghai Grand Theater, to its northeast the Shanghai Urban Planning Exhibition Hall, and to its south the Shanghai Museum. Flanked on both sides by 17-meter-wide greenbelts, People’s Avenue goes across the center of the square. The total green areas in the square reach 80,000 square meters. It is an oasis in the city.
Zhujiajiao Ancient Water Town
Known as the “Shanghai’s Venice”, Zhujiajiao is a typical ancient water town in the south of the Yangtze River. It first appeared as a village market during the Three-Kingdom Period over 1,700 years ago. Later, it became a bustling trade town in the Ming Dynasty. Today, visitors can still see many well-preserved streets, buildings, and local conditions and customs of the water region dating back to the Ming and Qing Dynasties. This is a little quiet town where people can find antiquity, leisure and tranquility.
Special Food and Products in Shanghai
Various Chinese cuisines and the main cuisines of different parts of the world have concentrated in Shanghai, which have given rise to the delicacies of Shanghai through replacement of the old by the new, co-existence or combination. The true Shanghai cuisine includes the household dishes, with traditional Shanghai flavors. In Shanghai, there is a lot of time-honored brands, such as Caosugong Ink, Duoyunxuan Gallery. The dumplings at City Temple, mooncakes at Xinhualou Restaurant, honey of Guanshengyuan Food Company, Big Rabbit milk candies, pear syrup at Yu Garden, vegetarian food at Gongdelin Restaurant are all time-honored special food and snacks in Shanghai.
II . Economy
(i) GDP figures
Shanghai GDP
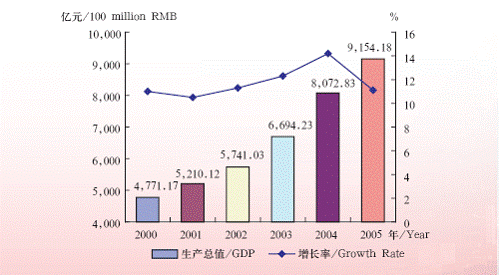
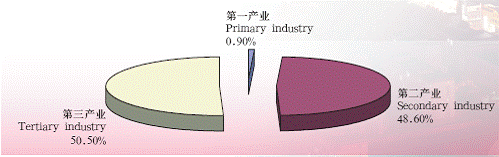
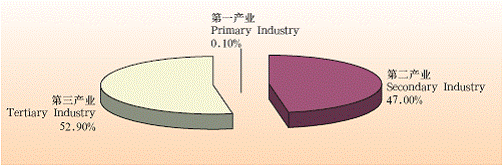
In 2005, the GDP of shanghai municipality reached 914.395 billion yuan. The city has further optimized its industrial structure, accelerating the development of modern services and advanced manufacturing industries. The ratio of the city’s primary industry, secondary industry and tertiary
industry had changed to 0.9:48.6:50.5 by the end of 2005.
Shanghai GDP and Growth Rate in 2000-2005
Ratio of Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Industries in Shanghai (2005)
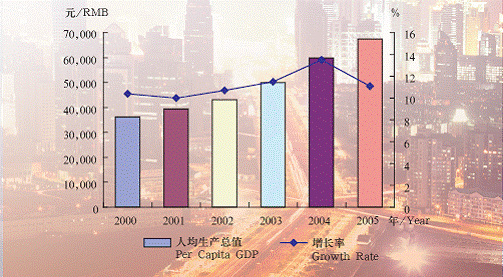
Shanghai Per Capita GDP and Growth Rate in 2000-2005
(ii) Industries, Services and Agriculture
Industries
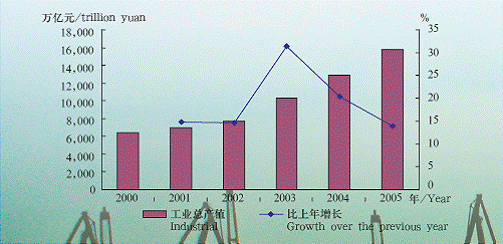
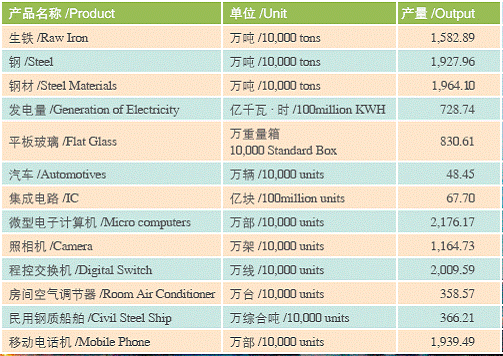
In 2005, Shanghai realized an industrial value of 1.68768 trillion RMB, maintaining 16 years of double digital growth. The city’s manufacturing sector boasts the advantage of complete range of industries, and necessary supporting services. According to the national business classification, Shanghai has all the 30 manufacturing categories. Shanghai has 161 out of altogether 169 industrial segments available in China. In 2005, the electronics, mechanics, light industries, petrol-chemicals, metal, and automotive industries realized 22%, 19.8%, 16.3%, 12.0%, 8.5% and 6.6% of the city’s total industrial value, while the rest accounted for 24.8%.
the Total Industrial Output and Growth Rate in Shanghai in 2000-2005
The Output of Main Industrial Products in Shanghai (2005)
Service Industry
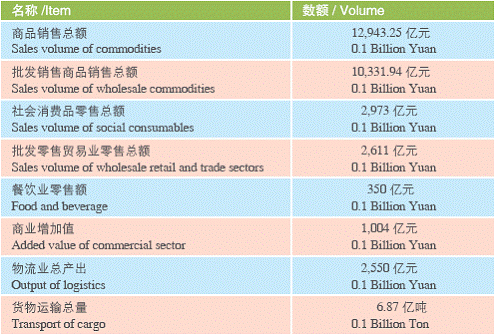
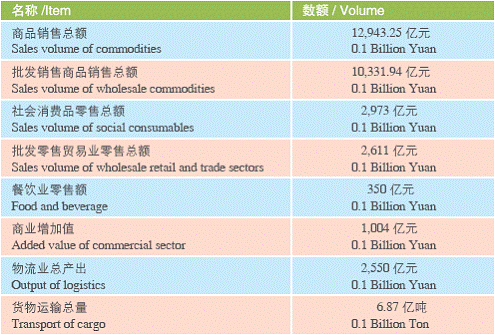
The tertiary industry in the city, the core of the modern service business, has witnessed steady development. In 2005, the six key sectors, namely, finance, wholesales and retails, real estate, transportation, logistics and postal services; information services and software, and boarding and catering, accounted for nearly 40% of the city’s GDP. Among the six, the proportion of the added value from wholesales and retails reached 9.1%, leading the tertiary industry. The financial sector in the city’s total stood at 7.5%. The figure with the transport, logistics and postal services reached 6.4%.
Data on Social Sectors(2005)
Agriculture
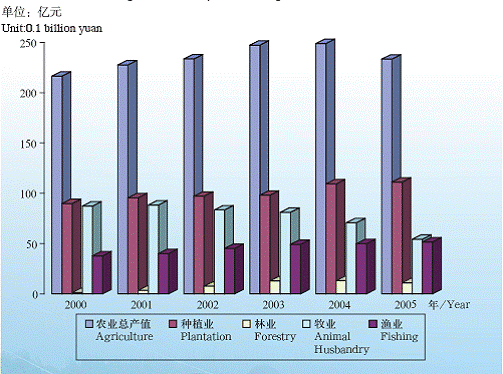
The rural areas of Shanghai have accelerated the readjustment of agricultural structure, focusing on pushing the factories into industrial parks, attracting residents into urban areas and adjusting farmland into large-scale farming operation.
Agriculture Output in Shanghai in 2000-2005
(iii) Business Data
Import and Export
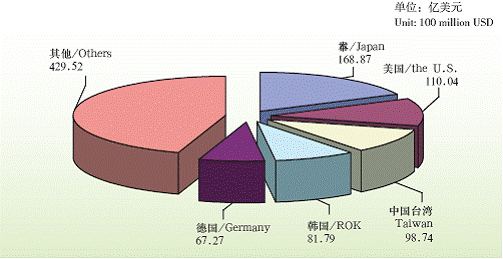
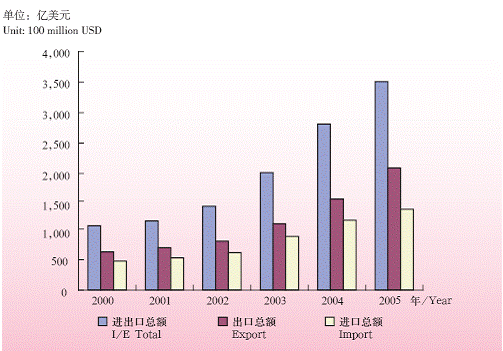
Since opening up, the international trade has been processed in an all-around way, multi-level and wide range fashion. Remarkable changes have happened on the scale, quality and management. In 2005, there are 186.365 billion USD trade volume, among which, 95.6 billion import and 90.7 billion USD export. Through the “Integrated Customs Clearance” Project, and“ E-Customs”, Shanghai has enhanced the port function of the city. In 2005, the import and export through Shanghai port reached 350.678 billion USD, among which, 138.248 billion are import and 212.43 billion export.
Shanghai Import and Export Value form 2000 to 2005
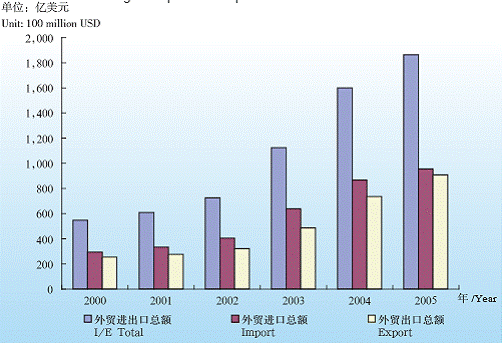
Shanghai’s Import from Overseas Countries and Regions
Import and Export through Shanghai Ports from 2000-2005
Shanghai’s Export to Overseas Countries and Regions
FDI
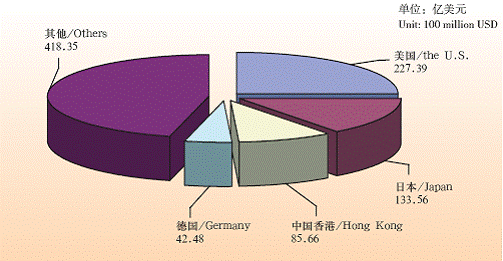
Since China’s reform and opening-up, FDI has continuously fl owed in to the city. In 2005, Shanghai approved 4,091 foreign-invested projects, with contractual capital of 13.83 billion USD, and paid-in capital 6.85 billion USD. By the end of 2005, Shanghai has approved 40,486 foreign-invested projects, with contractual capital of 99.96 billion USD, and paid-in capital 59.76 billion USD in total. The industry priority pattern the foreign investors prefer as follows: tertiary, secondary and primary industries. In 2005, 2,775 projects were in the tertiary industry, with contractual capital of 7.31 billion USD, accounting for 52.9% of the total; 1,308 projects are in the secondary industry, with contractual capital of 6.51 billion USD, accounting for 47%. 120 countries (regions) have FDI in Shanghai.
In 2005,485 out of Fortune 500 (excluding 15 local companies), 260 have investment in Shanghai, 232 have established their ventures. The area for the investment are mainly auto and auto parts, electronics and electric equipment, banking and insurance, and altogether 10 main industries.
Contracted Foreign Investment of Shanghai
Unit: 100 million USD
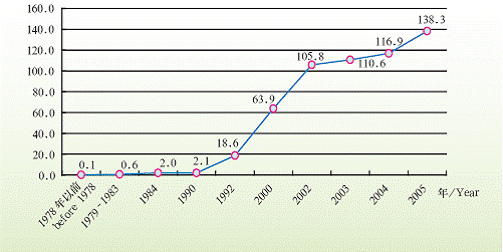
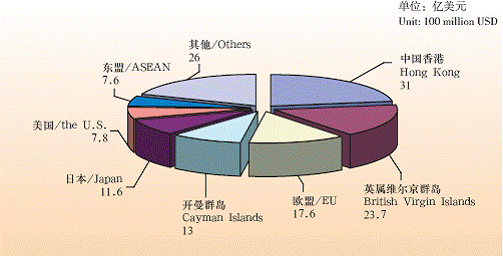
Contractual FDI by Overseas Countries and Regions in Shanghai (2005)
Unit: 100 million USD
Number of MNCs with Regional Headquarters, Holding Companies and R&D centers

Industry Structure of FIEs in Shanghai (2005)
Foreign Economic Cooperation
Shanghai companies have been accelerating the pace of“ going abroad”, while improving its technology content, widening its scope, and emphasizing on general contracting and integration of services. In 2005, the external investment by Chinese companies have reached 680million USD, setting up 5 R&D units, and newly-signed foreign contracted engineering projects and labor cooperation have been growing 50% and 74.8% respectively.
Foreign Economic Cooperation Projects (2005)
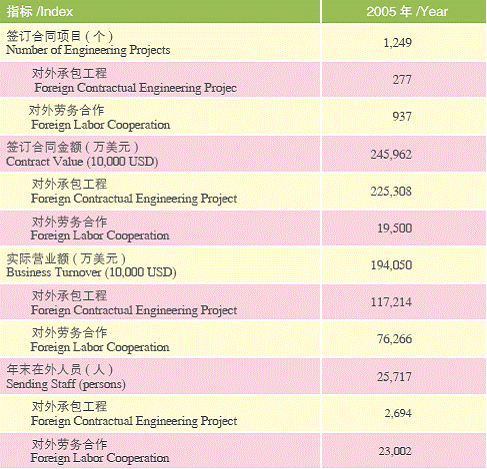
External Investment
Data on Shanghai’s Overseas Companies
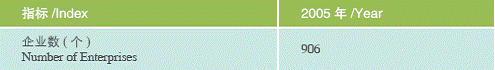
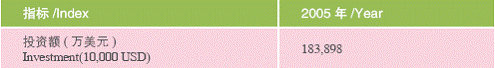
Import of Technology
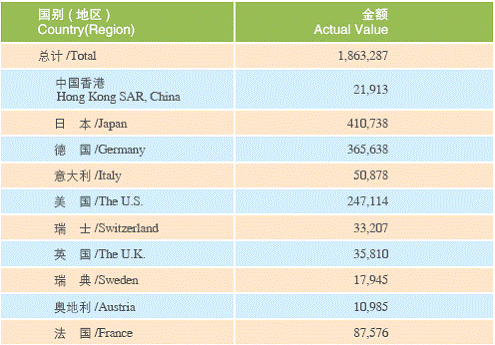
Since open up, Shanghai has made major efforts to import advanced production processes and technology equipment, facilitating the innovation and reform of enterprises and promoting the upgrade of the high-tech industry and its industry structure.
Commodities Distribution
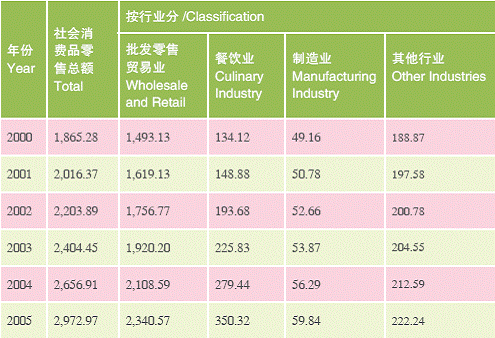
In 2005, the retail value of Shanghai social consuming goods summed up RMB 297.297 billion at a growth rate of 11.9% compared with the previous year, accounting for 4.43% of the whole nation. The retail value of the foreign invested commerce summed up RMB41.86 billion at an increase rate of 11.9% compared with the previous year. Among those newly established large scale supermarkets, foreign invested enterprises took more than 50%. Up to the end of 2005, a total of 67 foreign-invested large-scale supermarkets opened, accounting for 60% of the whole industry in the city, with their retail value shared 76% of the whole.
In recent years, Shanghai has endeavored to construct logistics facilities, logistic information and related policies, develop the third party logistic providers, put up major logistic zones, and accelerate the upgrade from traditional logistic industry to modern forms. From 2001 to 2005, the added value created by the local logistic industry has grown from 62.8 billion RMB to 117.5 billion RMB, accounting for 13% of the city’s total.
Actual Value of Imported Technology Equipment of Shanghai in 2005 Unit: 10,000 USD
Social Consumables Sales Volume (2000-2005) Unit: 100 million RMB
III . Investment
(i)Policy and Administrative Rules
Catalogue of Related Laws
Foreign Trade Law of the People’s Republic of China
Customs Law of the People’s Republic of China
Law of the People’s Republic of China on Import and Export Commodity Inspection
Law of the People’s Republic of China on Chinese-Foreign Equity Joint Ventures
Law of the People’s Republic of China on Chinese-Foreign Contractual Joint Ventures
Law of the People’s Republic of China on Foreign-Capital Enterprises Company Law of the People’s Republic of China
Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Entry and Exit Animal and Plant Quarantine
Law of the People’s Republic of China on Control of the Entry and Exit of Aliens
Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Control of the Exit and Entry of Citizens Securities Law of the People’s Republic of China
Income Tax Law of the People’s Republic of China for Enterprises with Foreign Investment and Foreign Enterprises
Individual Income Tax Law of the People’s Republic of China
Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Administration of Tax Collection
Environmental Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China
Law of the People’s Republic of China on Evaluation of Environmental Effects
Law of the People’s Republic of China on Promotion of Cleaner Production
Law of the People’s Republic of China on Prevention and Control of Desertification
Marine Environment Protection Law of the People’s Republic of China
Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Atmospheric Pollution
Law of the People’s Republic of China on Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution by Solid Waste
Law of the People’s Republic of China on Prevention and Control of Water Pollution
Law of the People’s Republic of China on Prevention and Control of Environmental Noise Pollution
Law of the People’s Republic of China on Prevention and Control of Radioactive Pollution
Frontier Health and Quarantine Law of the People’s Republic of China
Labour Law of the People’s Republic of China
Trade Union Law of the People’s Republic of China
Searching Website for the Related Laws
1. Searching System of Laws and Regulations of China (website of National People’s Congress of China)
http://law.npc.gov.cn:87/home/begin1.cbs
2. China Legislative Information Network System
http://www.chinalaw.gov.cn/jsp/jalor/ index.jsp
3. Ministry of Commerce
http://www.mofcom.gov.cn
The above-mentioned websites are for reference only.
(ii) Major Industries in Shanghai for Foreign Investment
1. Manufacturing Sectors
(1)Equipment Manufacturing
(2)Electronics and Telecommunication Equipment Manufacturing
(3)Automotive Manufacturing
(4)Modern Biological Technology and Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
(5)New Material
(6)Ship Manufacturing
(7)Petrochemical and refinery chemical manufacturing
(8)Advanced Steel Manufacturing
(9)Airplane Manufacturing
(10)Other industries suitable for city development
2. Services Sectors
(1)Financial Service
(2)Logistics
(3)Distribution
(4)Social Service
(5)Science, Research and Technology Service
(6)Real Estate
(7)Tourism
(8)Information and Consultation
3. Urban Infrastructure and Public facilities
4. Agriculture, Forestry, Animal Husbandry and Fishing
(Please consult www.investment.gov.cn for details)
(iii) Procedures for Enterprise Establishment
Basic procedures
Procedures Simplified Application for and Approval of Foreign-invested Projects
1. Regular Examination and Approval Procedures
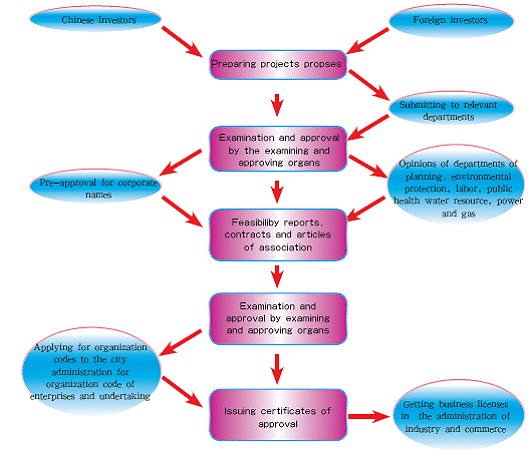
Examination and approval for below-mentioned three circumstances refers to the following work flow chart:
(1)Projects for examination and approval of relevant departments of the State of Council
(2)Projects with fundamental constructive contents
(3)Other projects regulated by the state
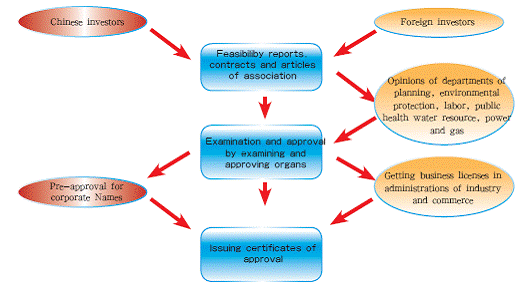
2 . Simplified Examination and Approval Procedures
According to“ Opinions on approval procedures and services for foreign invested projects in Shanghai”(2003), the examination and approval for Projects with no above-mentioned three circumstances shall enjoy simplified procedure, that is, the three steps for approval of Project Proposal, Feasibility Study, contracts, articles of associations will be merged into one-step approval.
(iv) Living Environment
Visa
For foreign investors’ planning business trip in China, they may ask their Chinese trading partner to apply for visa notice at the foreign affairs administration of the city where their Chinese partner is located. The visa notice is necessary for the visa application to the Chinese Embassy in the foreign investor’s own country.
Work and Residence Permit
Foreign invested enterprises are subject to apply for Employment Certification at Shanghai Labor and Social Security Bureau for their intended foreign employees. The Employment Certification is necessary for the application of working visa notice at Shanghai Municipal Foreign Economic Relations and Trade Commission. The employee shall apply for working visa at Chinese Embassy with the notice and certification, and complete the registration of employment at Shanghai Labor and Social Security Bureau within 15 days after arrival in China. The employment statement is compulsory for the foreign employee to obtain his Residence Permit at Entry-Exit Administration Bureau of Shanghai Public Security Bureau.
Urban Life
Shanghai has made remarkable progress in pollution control and environment protection and the city’s environment has greatly improved. In 2005, the city invested RMB 28.1 billion, or 3.07% of the city’s GDP, into environmental protection projects. As a result, the water quality in the city had been further improved. By the end of 2005, the city’s areas of parks and gardens amounted to 28,900 hectares. In total, 12,000 hectares were public green areas. The average per capita green area reached 11 square meters in the city and the green area coverage reached 37% of the city’s total territory.
By the end of 2005, there were 2,452 medical institutions of various categories in the city, of which 487 were hospitals (19 Sino-foreign equity or cooperative joint venture medical institutions), providing services to the domestic and overseas patients including those from Hong Kong and Macao. The multi-level medical service can meet various demand. There were 221 Sino-foreign jointly operated school-running institutions and projects in Shanghai in 2005.
There were 21 schools of children of foreign nationals, 5 local schools setting up their international divisions (4 senior high schools and 1 kindergarten), and primary and high schools and schools of children of foreign personnel accepted 18,300 foreign students. There were 26,200 foreign students in institutions of higher education. Altogether there were 44,500 foreign students
in Shanghai. The number of students from Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan studying in Shanghai were rising quickly, the number of the college students in Shanghai has reached 1,700 and the same policies as for local students gradually apply to them.
Shanghai maintains good social order through the operation of well-organized and highly efficient public security system. Shanghai Public Security Bureau 110 Emergency Call Center receives calls in 8 languages of English, German, Japanese, Russian, etc. The Emergency Reaction Center has been established with the joint efforts of Crime Call 110, Fire Call 119 and Traffic Control Platform, which proves efficiency in protection of the public security of the city.
Shanghai citizens live with rich art cultures. Shanghai Grand Theatre, Oriental Art Center, Shanghai Concert Hall, and other culture facilities have met all the infrastructure requirement of the world class symphony orchestra. It is the“ Shanghai-Style” culture, which incorporates things of diverse nature, combines indigenous with foreign elements, and integrates west with Chinese, that attracts many overseas groups to stage their performance in Shanghai.
Shanghai provides all the necessary supporting services, including grand scale shopping malls, super-markets, convenience stores, restaurants, body building centers, to make life in the city more convenient and comfortable.
Driving License
According to the traffic regulations of China , foreigners driving motor vehicle in China ought to hold the Motor Vehicle Driving License of the People’s Republic of China issued by the Chinese traffic administrative authorities .If you have your own country’s or international valid driving license, you may take your overseas valid driving license and Identity Card (Consular Officer Identity Card or Service Identity Card) to the Vehicle Administrative Office of the Shanghai Municipal Public Security Bureau and apply for a new driving license.
(v)Reference Prices of Basic Elements
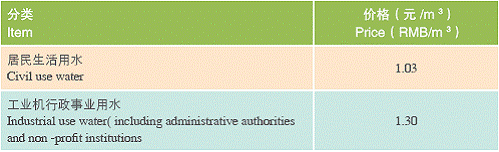
Water (tap water, industrial use water, etc.)
Charge for water supply

Charges of Using Drainage Facilities
Drainage for residential use is RMB 0.90 per cubic meter. When the total amount of using water surpasses 180 cubic meter in a year, the part over 180 cubic meter should be charged RMB 1.00 per cubic meter. Charges of Drainage for industry, administrative organization, service, and special use is RMB 1.10-1.40 per cubic meter.
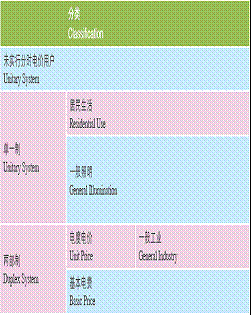
Electricity(Industrial use and Civil use)
Price of Electricity in Shanghai (Unit: RMB/KW.H)
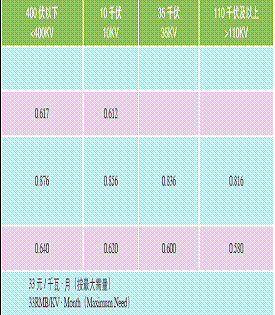
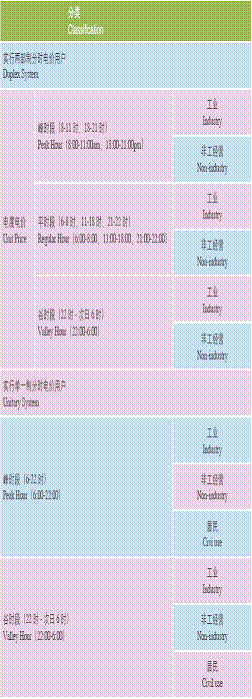
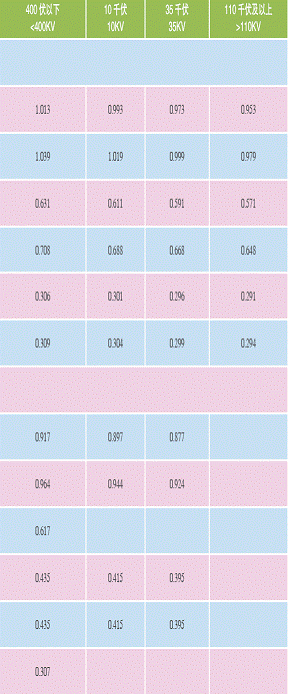
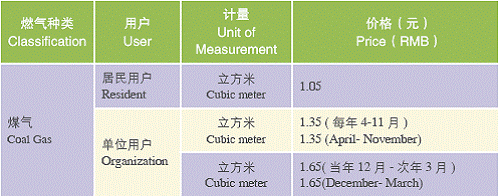
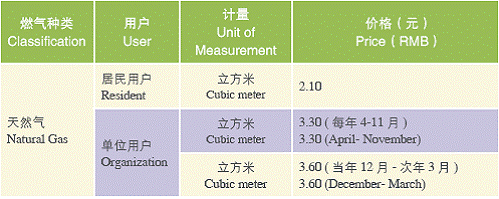
Gas Price
Price Index for Gas
Phone Charges
Price index for Telephone users


Labor Policies
Wages, Insurance and Welfare of Employees
1. Foreign-invested enterprises(FIE) can at their discretion determine company organization and personnel deployment according to its own requirement. However, the application for the employment of staff from other provinces and cities, Taiwan, Hong Kong and Macao and expatriates shall be forwarded to Shanghai labor and Social Security Bureau for approval.
2. FIE is authorized to arrange the wage system, forms of payment, allowances and compensation for its employees, as long as they met the minimum requirement by Shanghai Municipal Government released by September 2006, which is 750 RMB/Month. Please consult Shanghai Labor and Social Security Bureau ( www.12333.gov.cn) for more details with reference to different industries and employee qualifications.
3. Social Insurance:FIE is subject to apply social insurance for its employees.
Basic Pension
The monthly base is calculated according to the employee’s monthly average wages of the previous year. The basic pension comprises of 8% of the base paid by the employee, and 22.5% of the base paid by the employer.
Unemployment Pension
1% of the base paid by the employee and 2% of the base paid by the employer.
Medical Insurance
2% of the base paid by the employee, and 12% of the company’s Chinese employee’s average monthly wage paid by the employer.
Social Insurance for Small Towns in Shanghai
“Interim Measures of Social Insurance for Small Towns in Shanghai” came into force on October 20th, 2003. The measures apply to employers in the suburbs of the city and employees with Shanghai citizenship, and to other people approved by shanghai Municipal Government. Employer shall pay 24% of the employee’s income for basic social insurance, which include 17% for pension insurance, 5% for medical service insurance, and 2% for unemployment insurance. Procreation Insurance is exempt, while Insurance for employee’s injury during employment shall be subject to regulation separately promulgated.
4. Housing fund:7% of the company’s Chinese employee’s average monthly wage paid by the enterprises, 7% paid by employee.
Land Policies
The State Council has released new notice on land control, in which the minimum land use fees for various industrial use has been promulgated and published. The minimum price should be no less than the total land cost, including the obtainage, initial stage development and other regulated fees. The land for industrial use should be obtained through bidding procedure, and the bidding price should be no less than published minimum fee.
IV. Development Zones
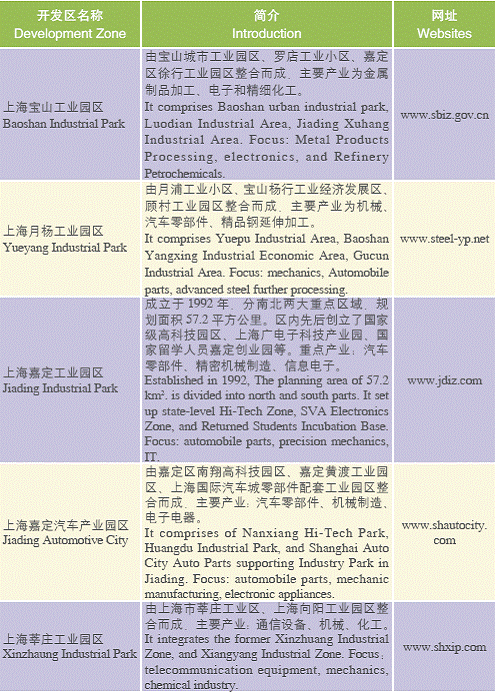
Shanghai Development Zones
State-level Development Zones
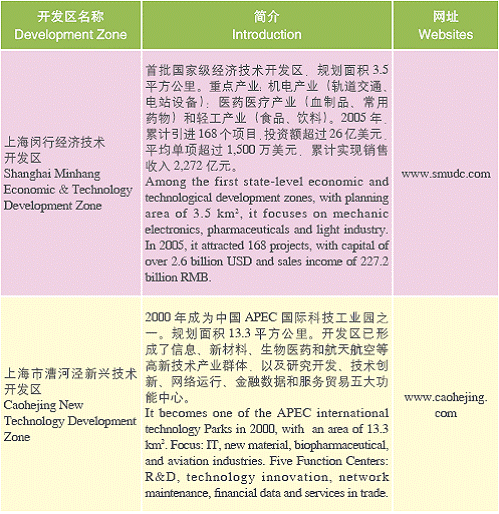


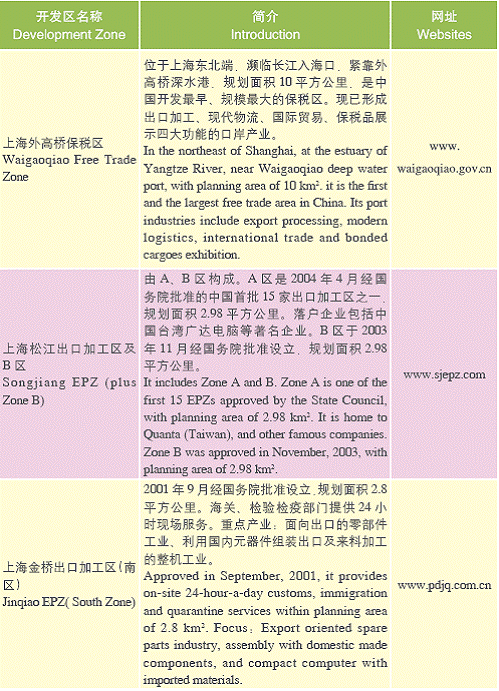

Municipal Level Development Zones



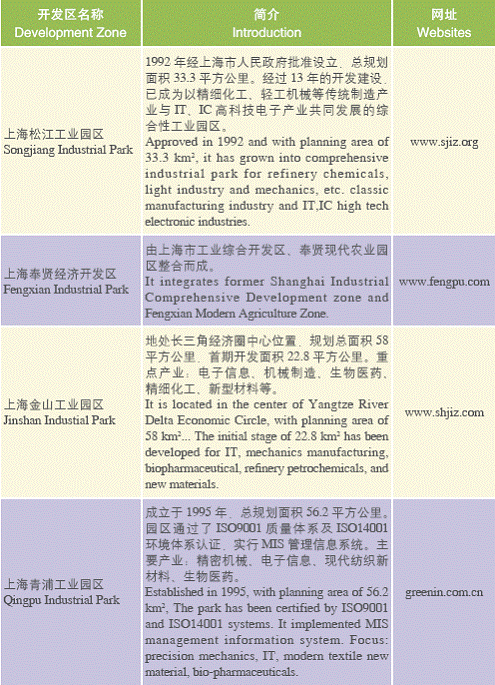
(ii)Related Organizations
Entry-Exit Administrative Organizations

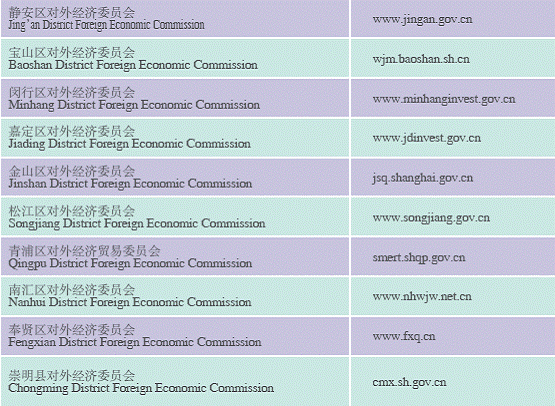
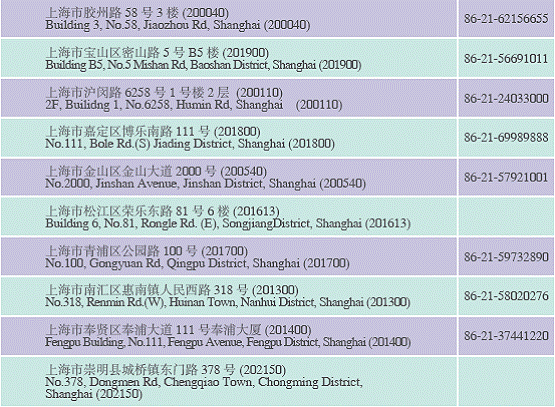
Commercial Organizations
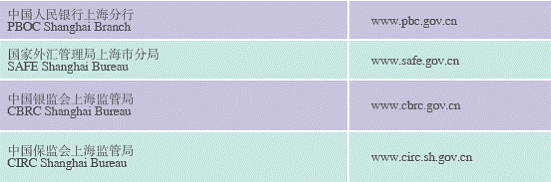
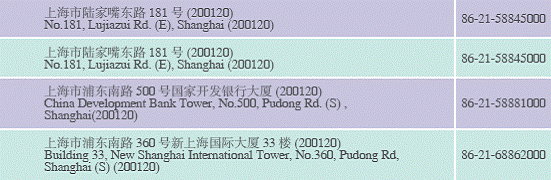
Financial and Foreign Exchange Organizations

Other Service Organization
(iii)Government Websites
(iv)Websites for Attraction of Foreign Investment

Appendix
Hotels and Restaurants

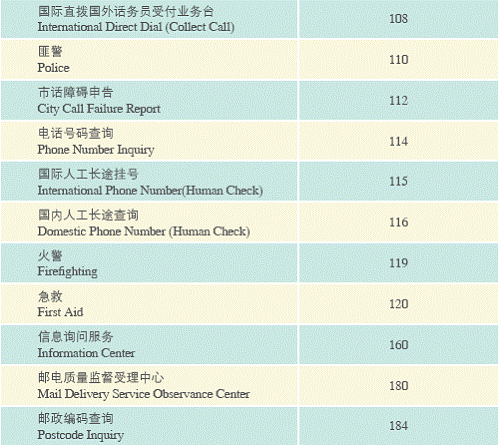
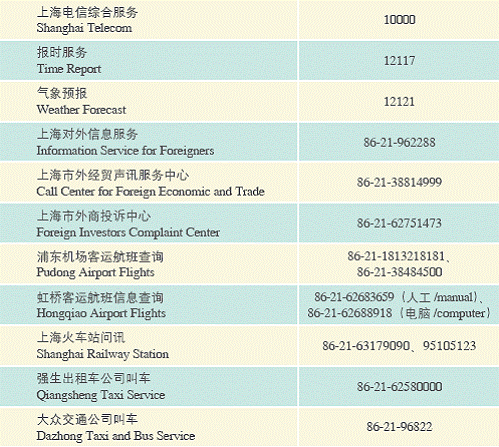
Emergency and Inquiry Numbers
(Ministry of Commerce)